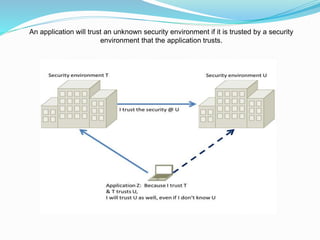
This document discusses mobile security and provides tips to stay safe. It begins with an introduction on how mobile phones are now used for more than calls and texts, and contain private data. It then covers security issues like physical theft, unencrypted voice calls and texts, and identifying IMEI numbers. The document details types of mobile security including device security measures like locks and remote wiping, and application security such as encryption and authentication. Mobile threats are reviewed like malware, phishing, and network exploits. Finally, tips are provided such as only downloading from trusted sources, setting passwords, using security tools, and being aware of unusual phone behaviors.