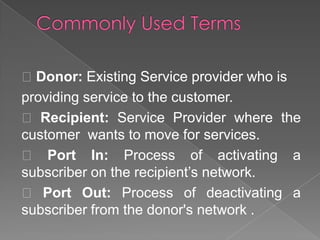
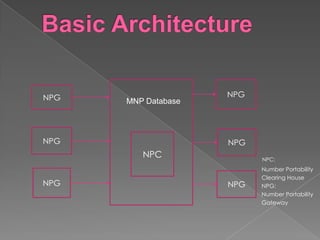
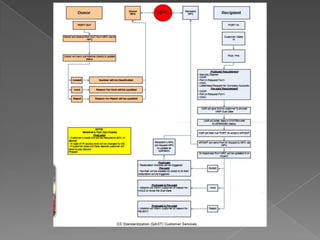
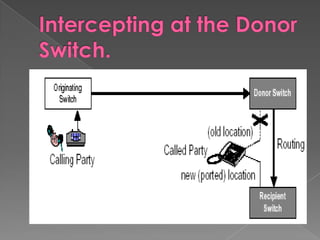
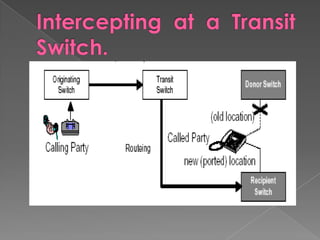
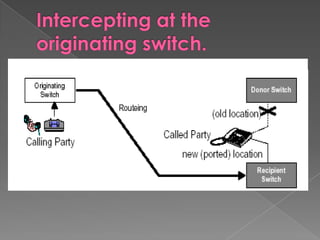
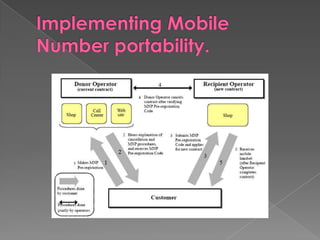
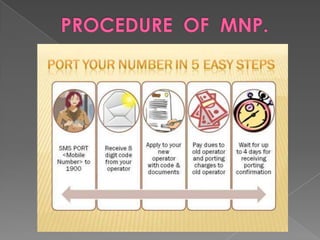
MNP, or mobile number portability, allows cellular users to change their mobile service provider while keeping their original phone number. It involves a port out process to deactivate a subscriber from their existing provider and a port in process to activate them on the new recipient provider's network. The porting transaction is facilitated through a number portability clearing house and gateways to intercept and route calls to ported numbers on the new provider's network.