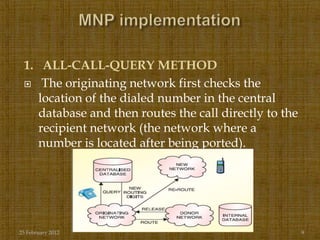
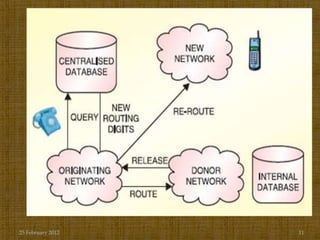
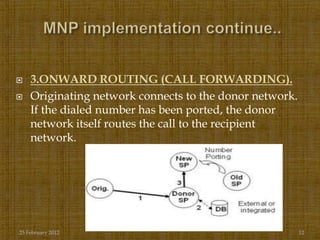
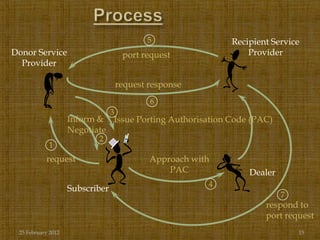
Mobile number portability (MNP) allows mobile subscribers in India to change their service provider while retaining their existing phone number. The document discusses how MNP benefits consumers by making it easier to switch providers for better plans or service without changing their number. It also provides details on the MNP process, including how porting requests are handled through a central reference database and the timeline of 4-6 days for a number to be ported to a new provider. Mobile operators are expected to utilize more aggressive advertising strategies under MNP to attract customers from other networks to migrate to their network.