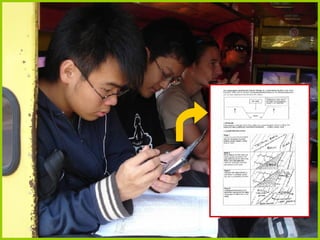
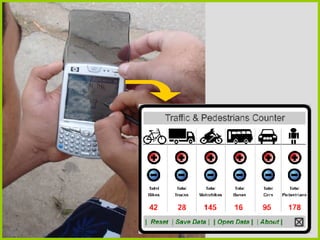
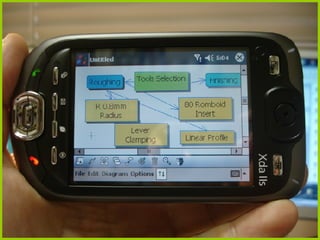
This document discusses the educational opportunities provided by mobile technologies. It outlines various functions of handheld devices such as cameras, internet connectivity, and additional applications. Studies are presented that used handhelds for file sharing, feedback, course delivery, field trips, and more. The author's own study identified key affordances of handhelds including multimedia access, connectivity, capture, representation, and analytics. The conclusion states that mobile technologies create educational opportunities and institutions should support students' use of these technologies for learning.



































![Thank you for attention! Q&A THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Faculty of Education Dr. Daniel Churchill Assistant Professor Email: [email_address] Phone: + 852.2859.1141 Web: http:// www.learnactivity.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobile-jakarta-by-daniel4887/85/Mobile-Jakarta-By-Daniel-41-320.jpg)