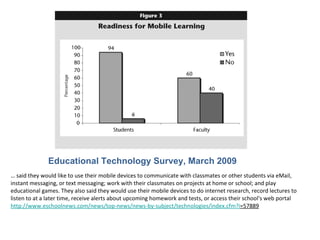
The document discusses using mobile technologies in the classroom and for learning. It defines mobile learning (m-learning) as using devices like PDAs, tablets, and cellphones to deliver modularized information and learning objects anywhere and anytime. Some benefits mentioned include extending learning outside the classroom, linking people and places, and supporting lifelong learning through just-in-time access to resources. Examples provided include mobile wikis, historical tours, citizen activism, and collecting real-time data. The document also discusses how different mobile devices and apps can support various learning theories and styles.


















![Contact Anne-Marie Armstrong [email_address] Kimberly Conely](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmcinteractives-090617124409-phpapp02/85/Nmcinteractives-Handhelds-21-320.jpg)