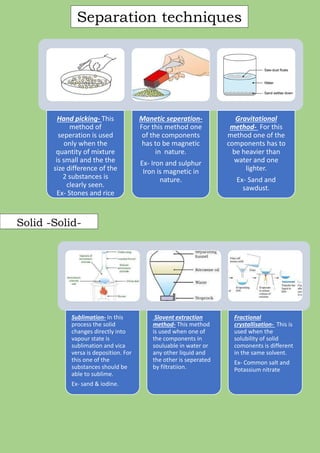
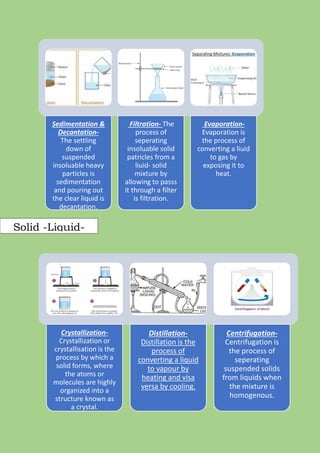
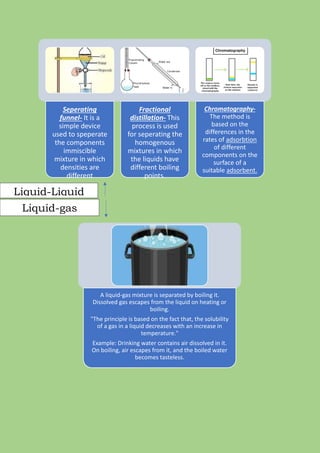
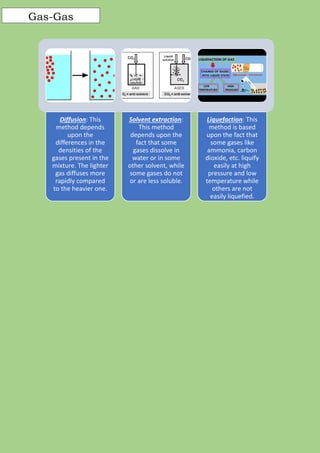
A mixture is formed when two or more pure substances are mixed without undergoing a chemical change. Mixtures can be either homogeneous, where the components are uniformly distributed, or heterogeneous, where the components can be seen separately. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated physically. Common separation techniques include filtration, evaporation, crystallization, distillation, and centrifugation which separate mixtures based on differences in physical properties like solubility, density, and boiling point.