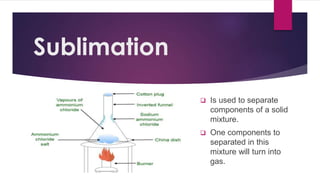
The document outlines various methods for separating mixtures, including filtration, sedimentation, decantation, evaporation, distillation, magnetism, crystallization, sublimation, and chromatography. Each method is described with examples of its applications, such as water purification and crude oil processing. Special techniques like chromatography are used in various industries, while common procedures rely on physical properties of the components.