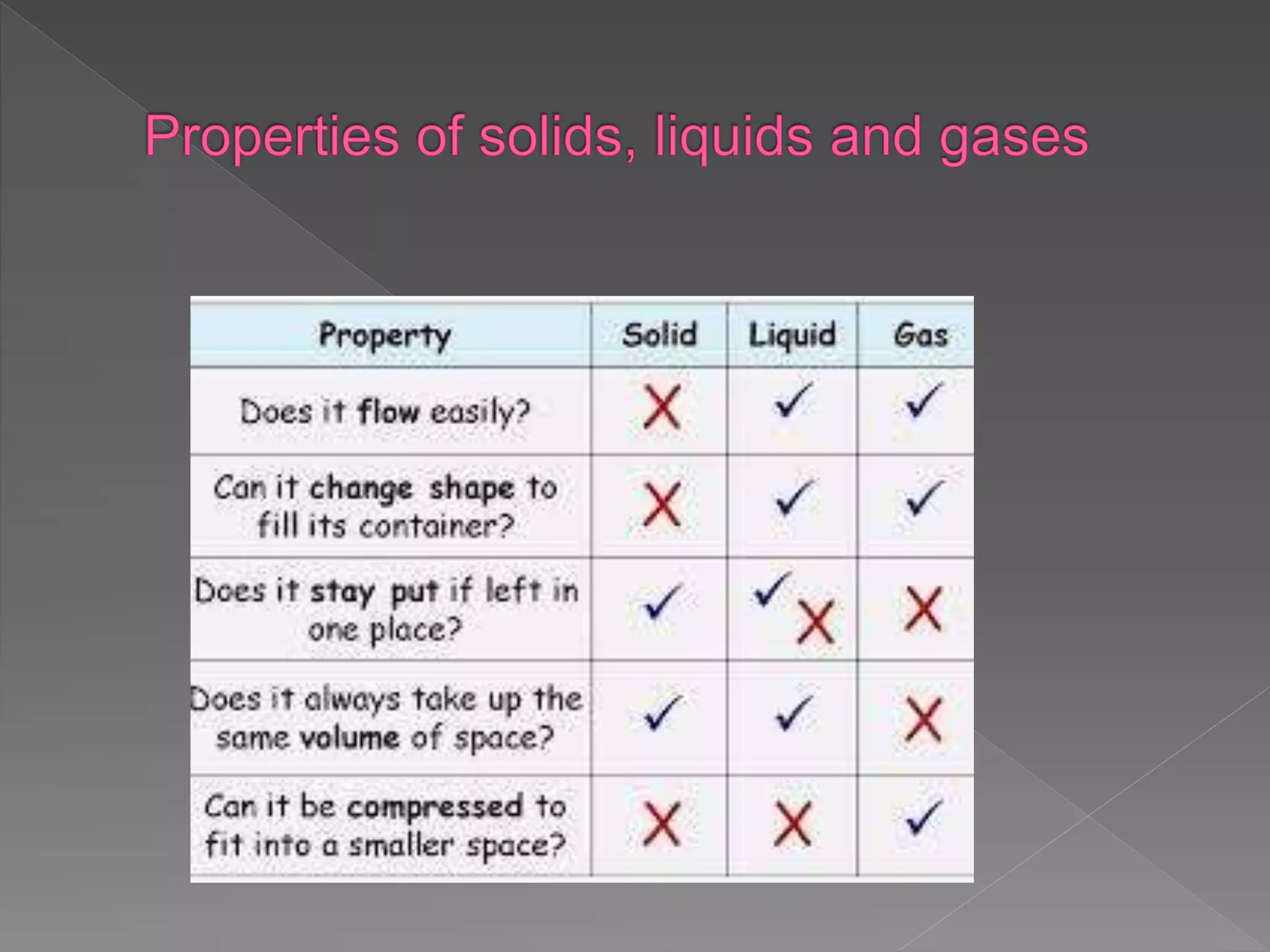
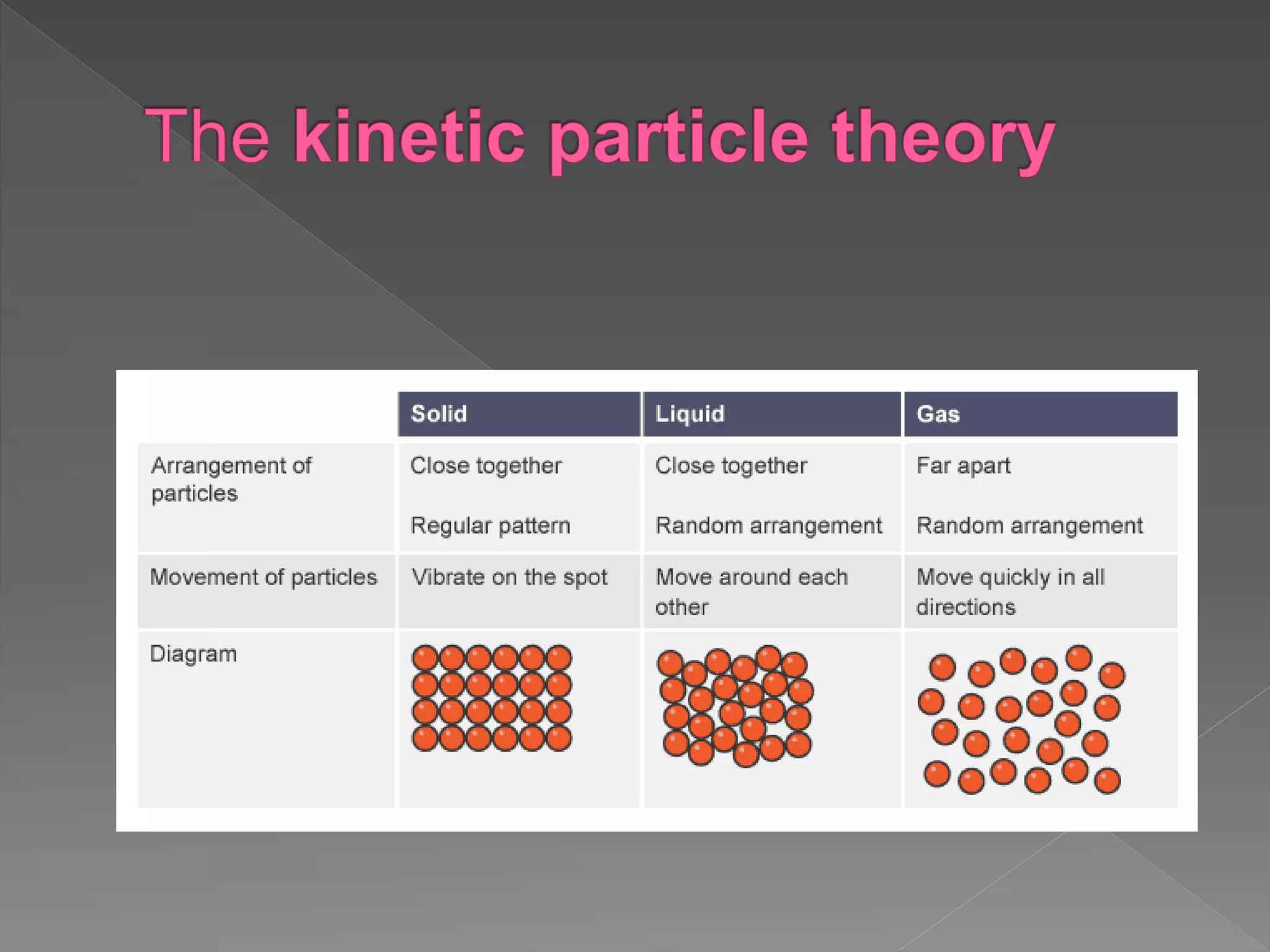
The document outlines the IGCSE Chemistry syllabus, specifically focusing on the properties and behaviors of solids, liquids, and gases, along with diffusion and changes of state. It explains the structure of matter, particle arrangements, and the kinetic theory as the basis for understanding how different states of matter behave. Additionally, it details the exam components including multiple-choice questions and written answers, along with weightage for each paper.