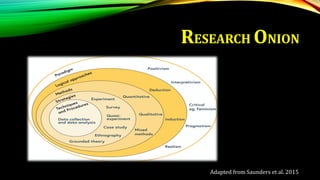
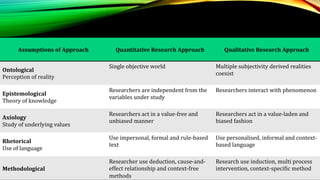
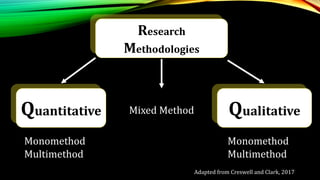
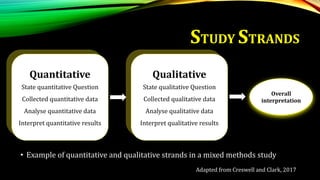
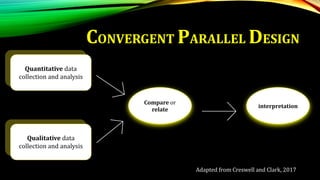
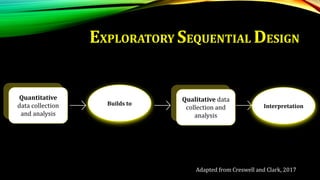
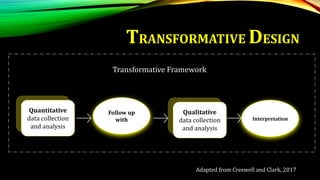
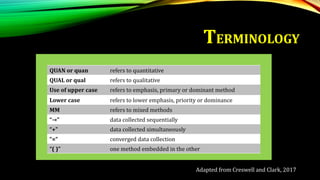
This document provides an overview of mixed methods research. It defines mixed methods as an approach that involves collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data to better understand research problems. The document discusses key aspects of mixed methods research such as common designs, advantages and challenges. It also covers topics like paradigm assumptions, strategies for mixing methods, and evaluating mixed methods studies. Major mixed methods designs introduced include convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential designs.