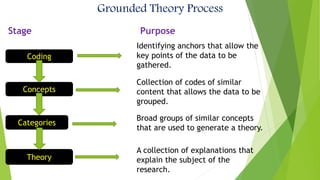
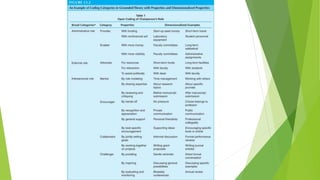
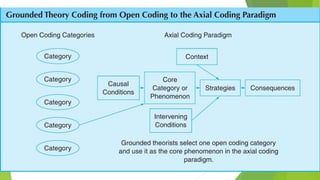
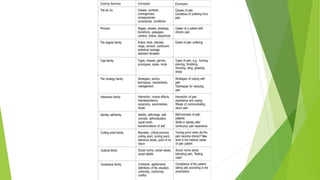
Grounded theory is a qualitative research method that aims to develop theories inductively from data. It begins with data collection and analysis to allow concepts and theories to emerge from the data rather than testing a predetermined hypothesis. Grounded theory was developed in the 1960s by sociologists Glaser and Strauss and has since split into different paradigms including Straussian, Glaserian, and Constructivist approaches. The key aspects of grounded theory include coding data through open, axial, and selective coding to develop categories and concepts into a theoretical framework or model.