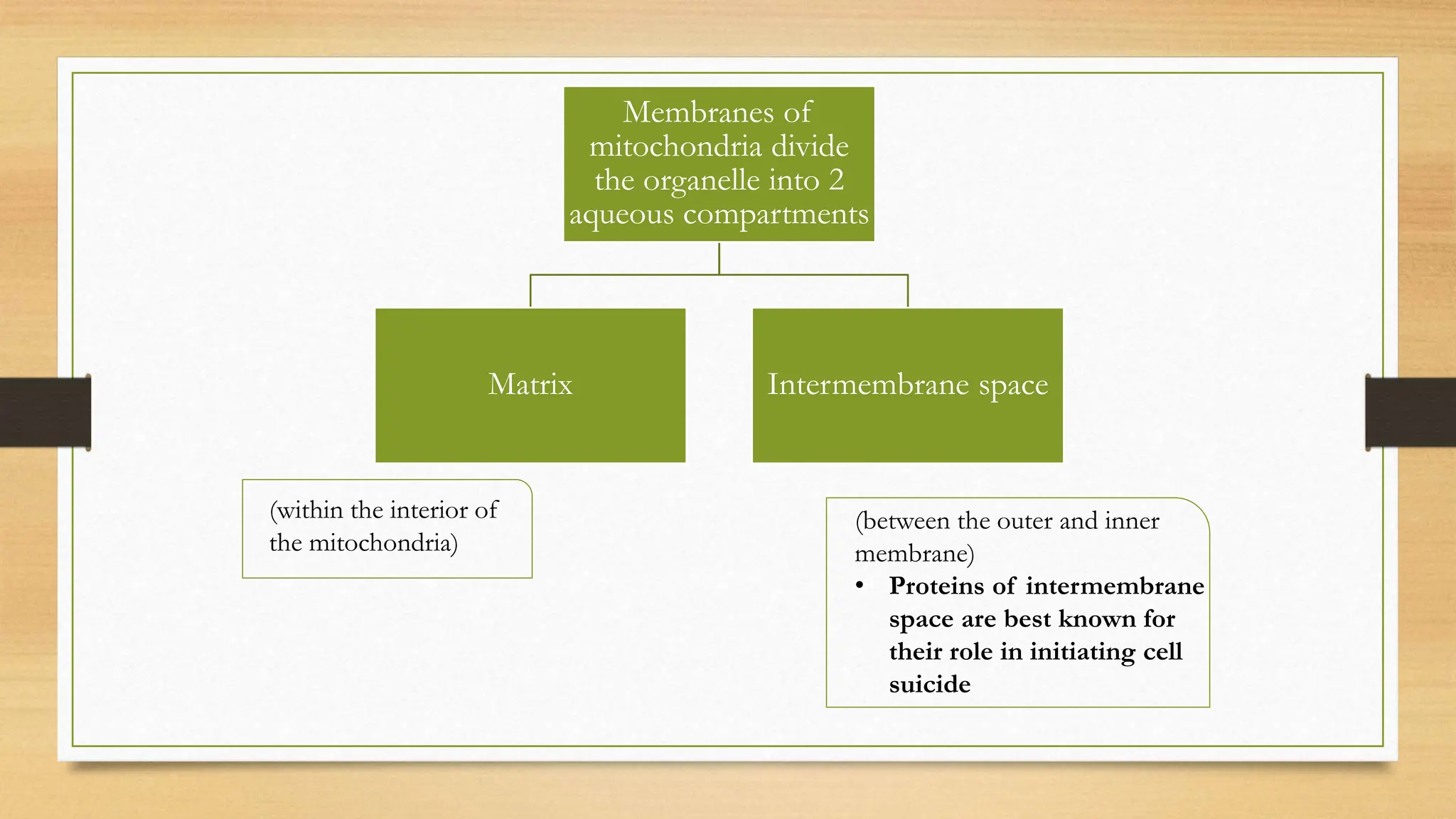
Mitochondria are organelles that generate ATP through aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells. They have an outer and inner membrane that form compartments and invaginations called cristae where the machinery for ATP production is located. Mitochondria play key roles in energy production, synthesis of molecules, calcium ion transport, and regulating cell death. They have their own DNA, ribosomes, and mechanisms for expressing genes to produce some proteins required for their functions.