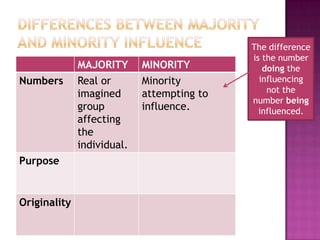
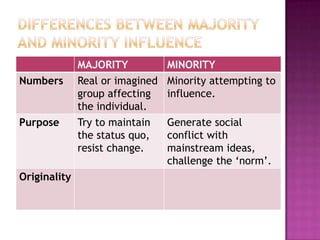
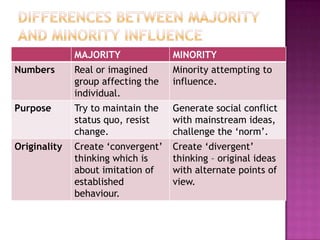
This document discusses how minorities can influence majorities through history examples like suffragettes, Christianity, and civil rights movements. It explains that minorities who are active, organized, and consistent can create social conflicts and uncertainties that lead to societal changes over time, even though they start as a small group. The key differences between majorities and minorities are numbers, purposes, and approaches to thinking - with minorities challenging existing norms through divergent thinking and new ideas.