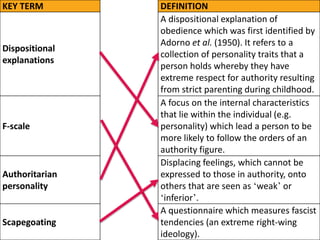
Elms and Milgram's research found that participants in Milgram's obedience study who fully obeyed the experimenter scored higher on the F-Scale questionnaire, which measures authoritarian personality traits. The F-Scale is problematic because it is subject to social desirability bias, where participants may answer in a way that makes them appear less authoritarian. Additionally, less educated people are more likely to display authoritarian traits, calling into question whether authoritarian personality truly causes obedience or if other factors like education are more influential.