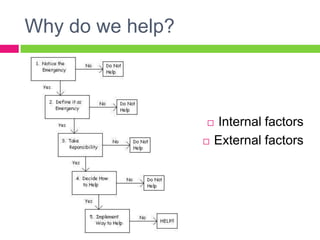
Prosocial behavior refers to voluntary actions that benefit others or society, such as helping, sharing, and cooperating. It is central to healthy social groups and is motivated by empathy. Research on prosocial behavior originated with studies on bystander effects during crimes and emergencies. Current research examines biological, motivational, cognitive, and social factors influencing prosocial acts through theories like empathy-altruism, negative state relief, kin selection, and reciprocal altruism. Volunteering has been associated with benefits to happiness and health.