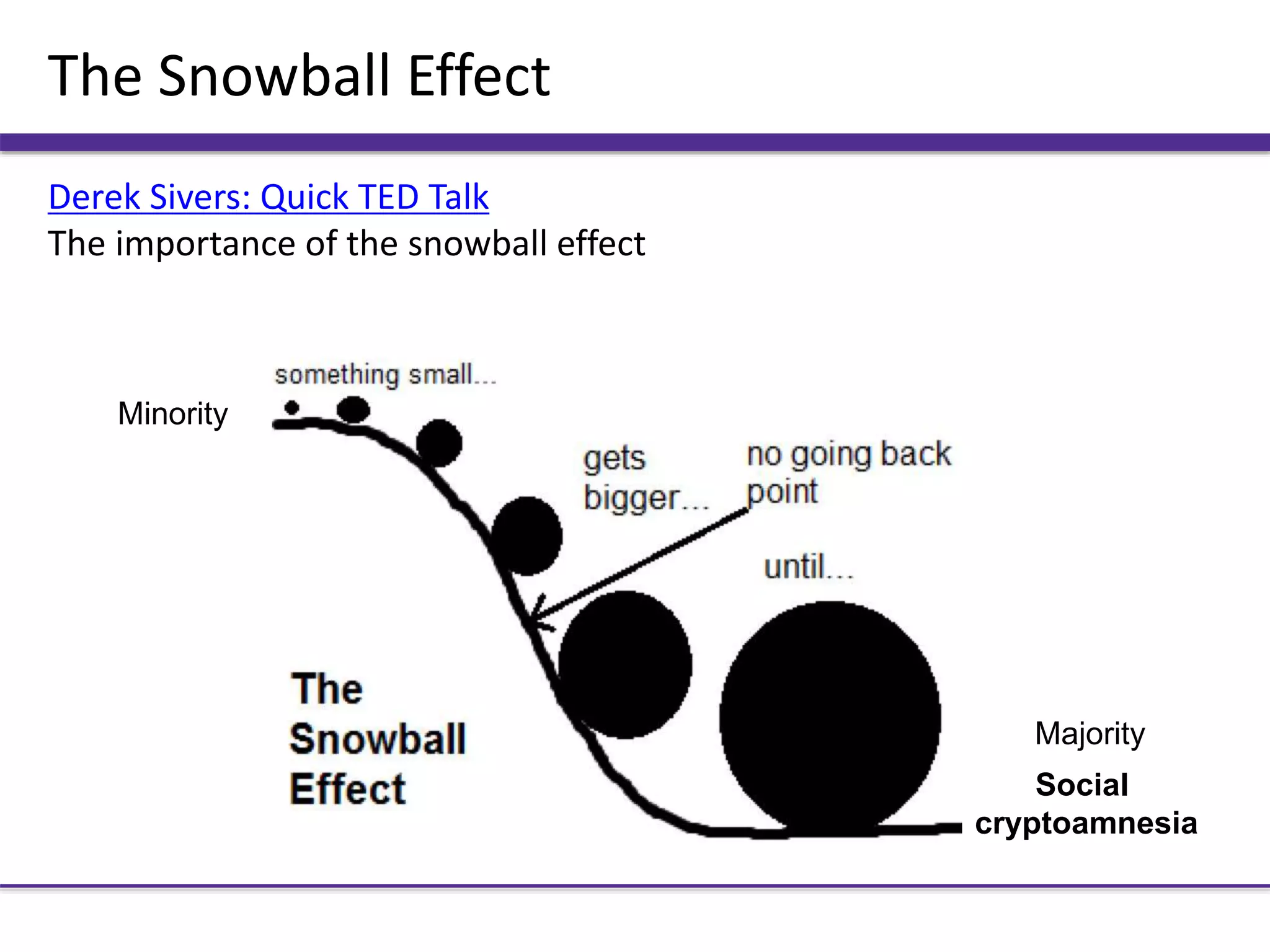
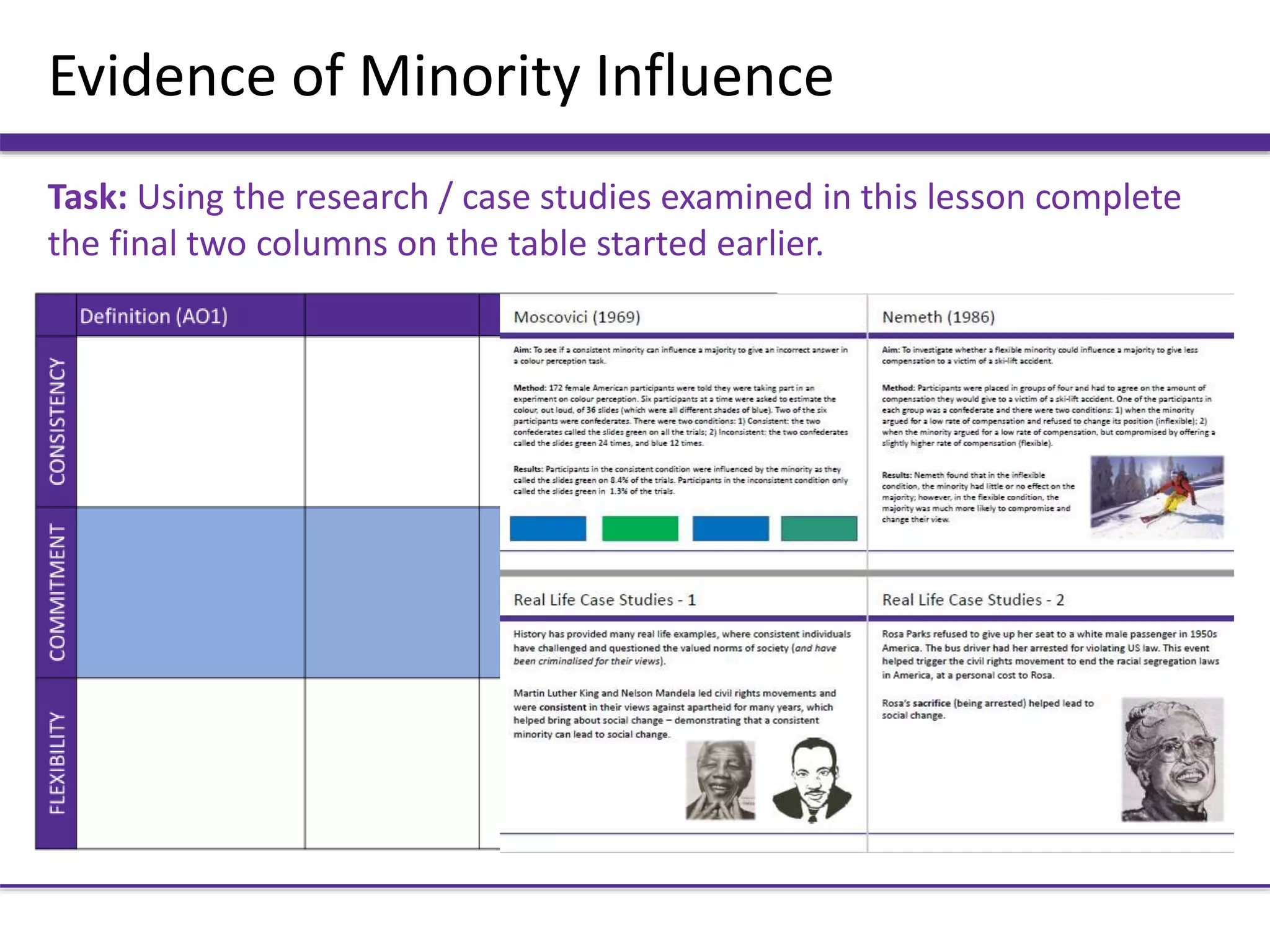
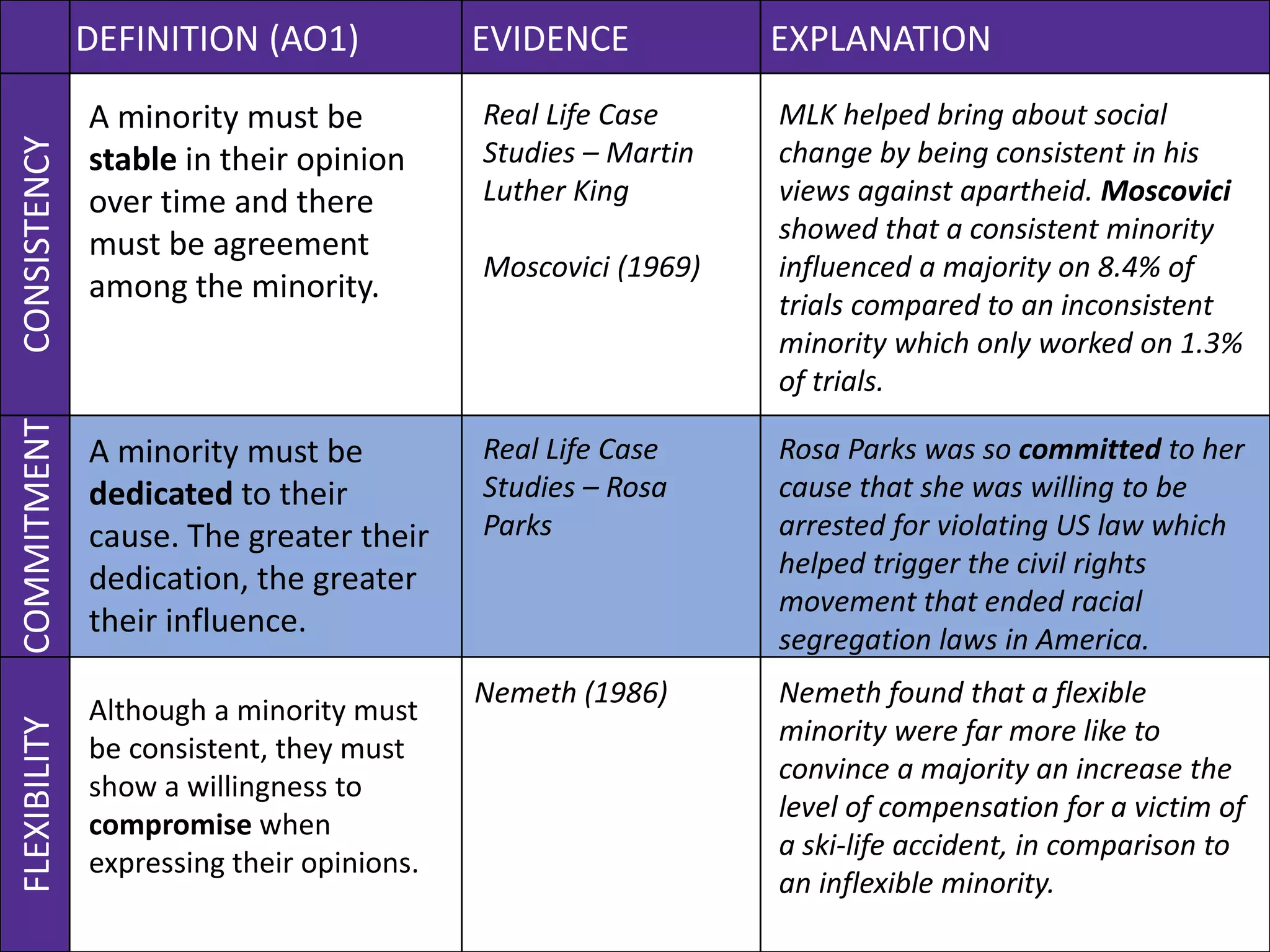
This document outlines key aspects of minority influence, including consistency, commitment, and flexibility. It discusses research by Moscovici from 1969 that found a consistent minority was more influential than an inconsistent one. Real-life examples include Martin Luther King Jr.'s consistent views influencing the civil rights movement, and Rosa Parks' commitment sparking further action. The document also discusses how a flexible minority in Nemeth's 1986 study was more persuasive than an inflexible one.


![Application (AO2)
With reference to the article above, explain how social influence [minority
or even majority influence] leads to social change. (6 marks)
The following article appeared in a newspaper:
Britain’s views on homosexuality – the biggest social change of the last 30 years?
In the UK, views on homosexuality have changed significantly in recent times.
Thirty years ago, almost two-thirds of the British public opposed same-sex
relationships because they were ‘morally wrong’. These days, homosexuality is
accepted and the majority of British people support recent changes to the laws on
gay marriage and adoption.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isuzeyutl6zkn1zzny1w-signature-8d7f6ae105fb68a50b755064649f8315d25cfd46c1598ee1fe358b9809ed2d2c-poli-181229215521/75/09b-minority-influence-social-change-pp-part-2b-6-2048.jpg)