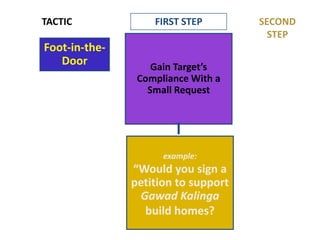
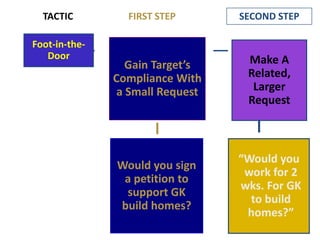
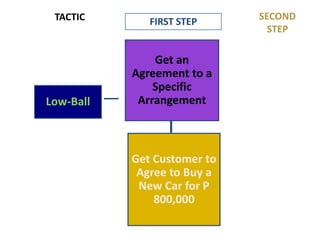
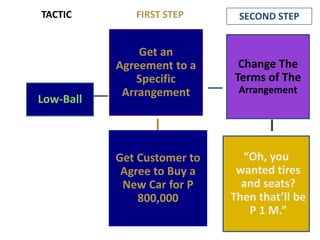
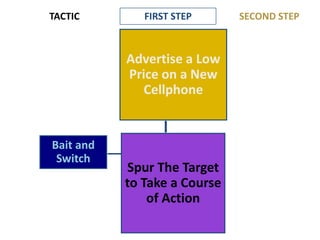
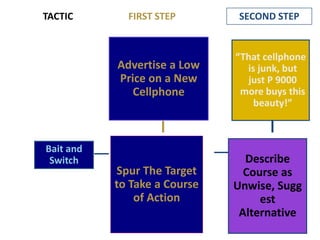
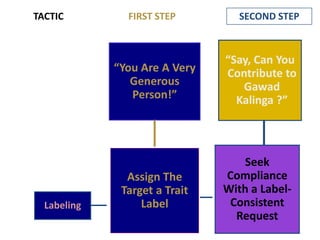
This document provides an overview of key concepts in social psychology. It defines social psychology as the scientific study of how individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by real, imagined, or implied social contexts. Some key topics covered include social influence, conformity, compliance, social norms, and research studies such as Asch's conformity experiments and Milgram's obedience studies. The document discusses how social factors like group pressure, authority, and reciprocity can influence individual attitudes and behaviors. In summary, it introduces social psychology concepts relating to how social environments and other people shape individual cognition, interaction, and performance.