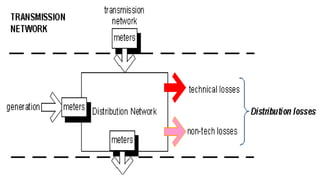
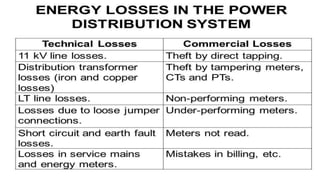
The document discusses electrical losses in distribution systems, highlighting technical losses categorized into fixed and variable types. Fixed losses, which are not affected by the load current, account for a significant portion of total losses and arise from sources like leakage and open circuit losses, while variable losses are related to load current. It also suggests several strategies for minimizing these losses, including proper planning, appropriate equipment selection, regular maintenance, and load management.