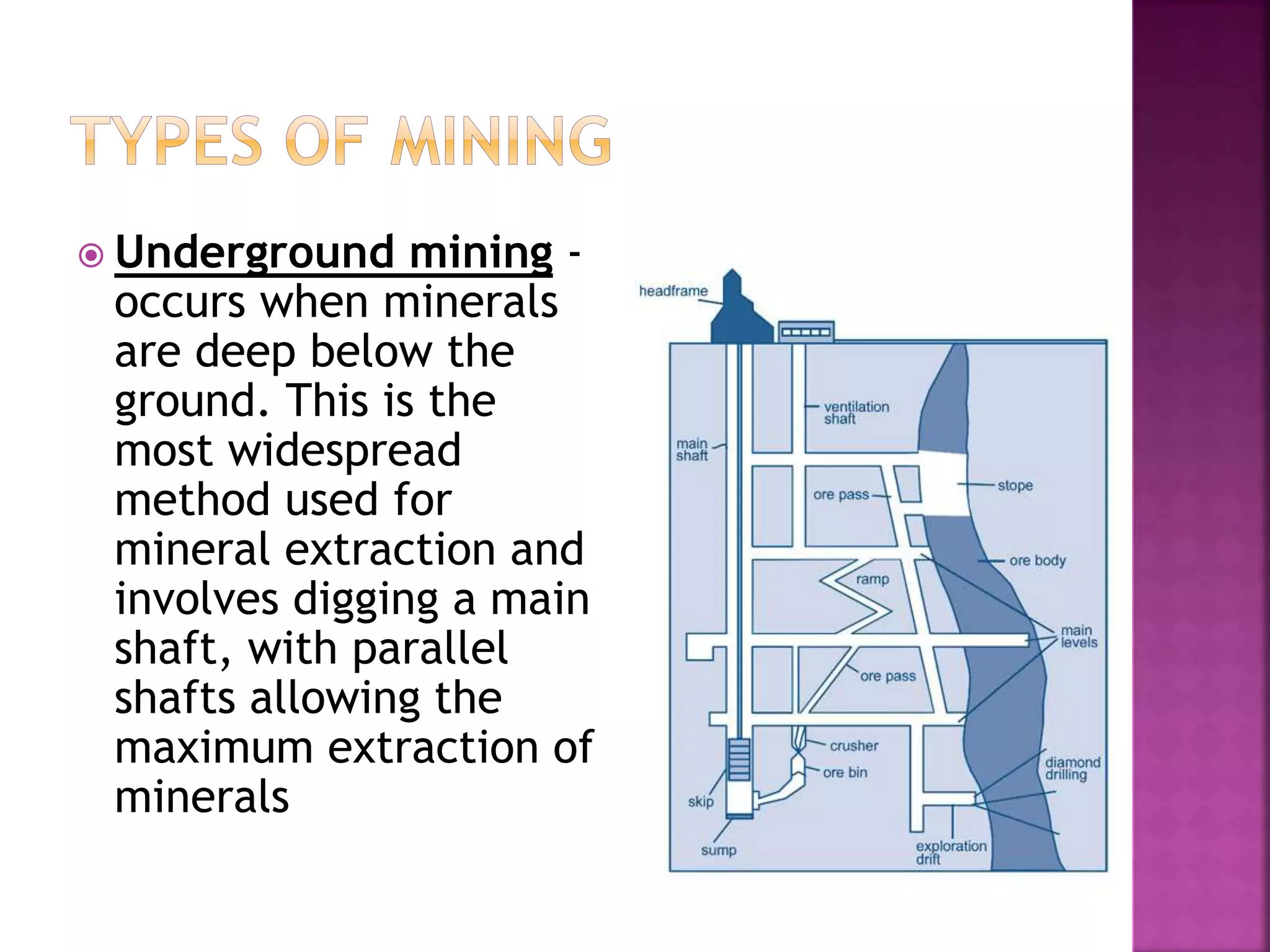
This document defines different types of minerals and mining techniques. It discusses the criteria for a mineral, including being naturally occurring and having a crystalline structure. It defines identified resources, undiscovered resources, and reserves. It then describes various mining methods like underground mining, hydro-mining, and opencast mining. Finally, it outlines some environmental impacts of mining like water pollution, acid mine drainage, deforestation, and effects on groundwater.