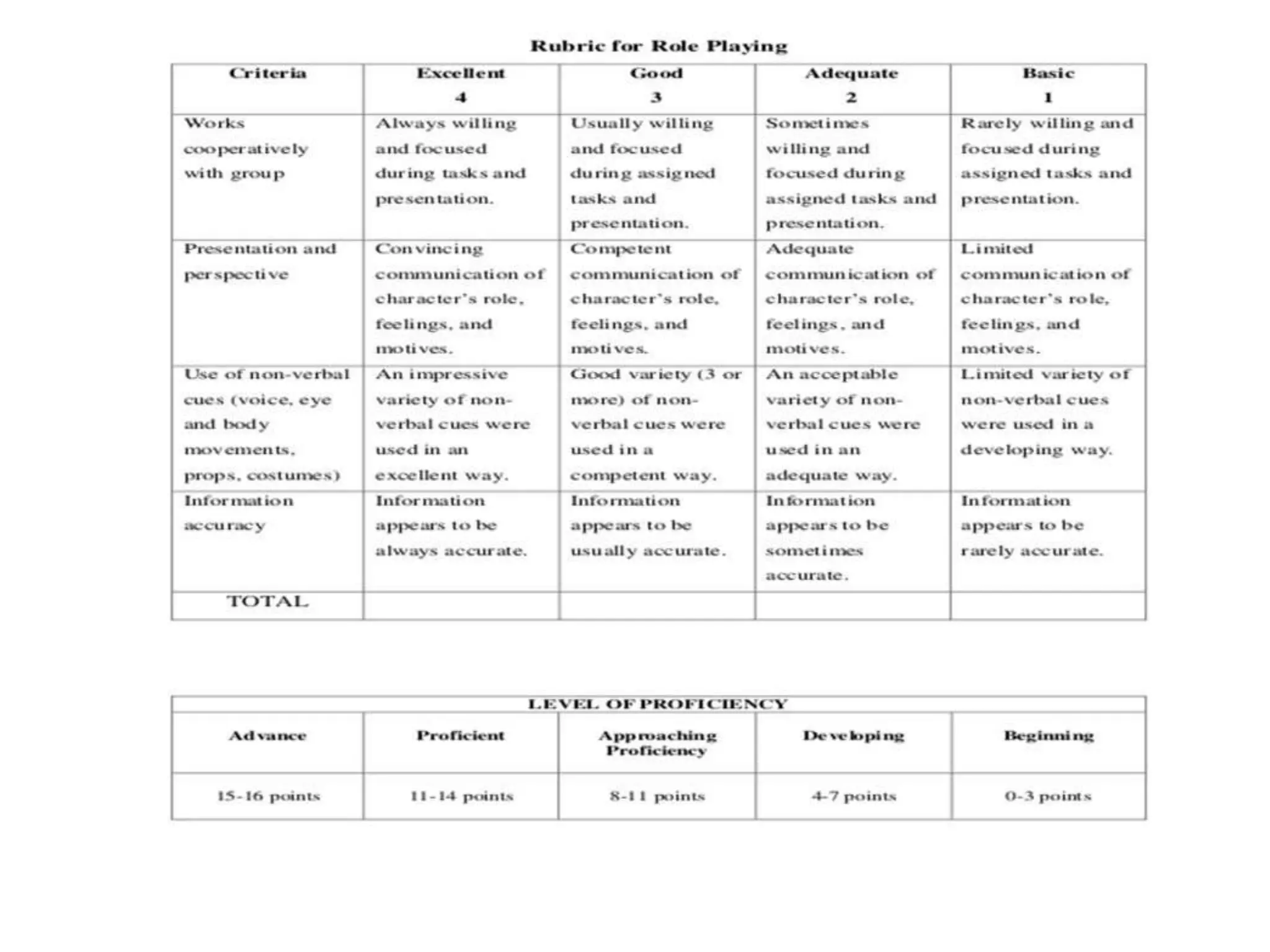
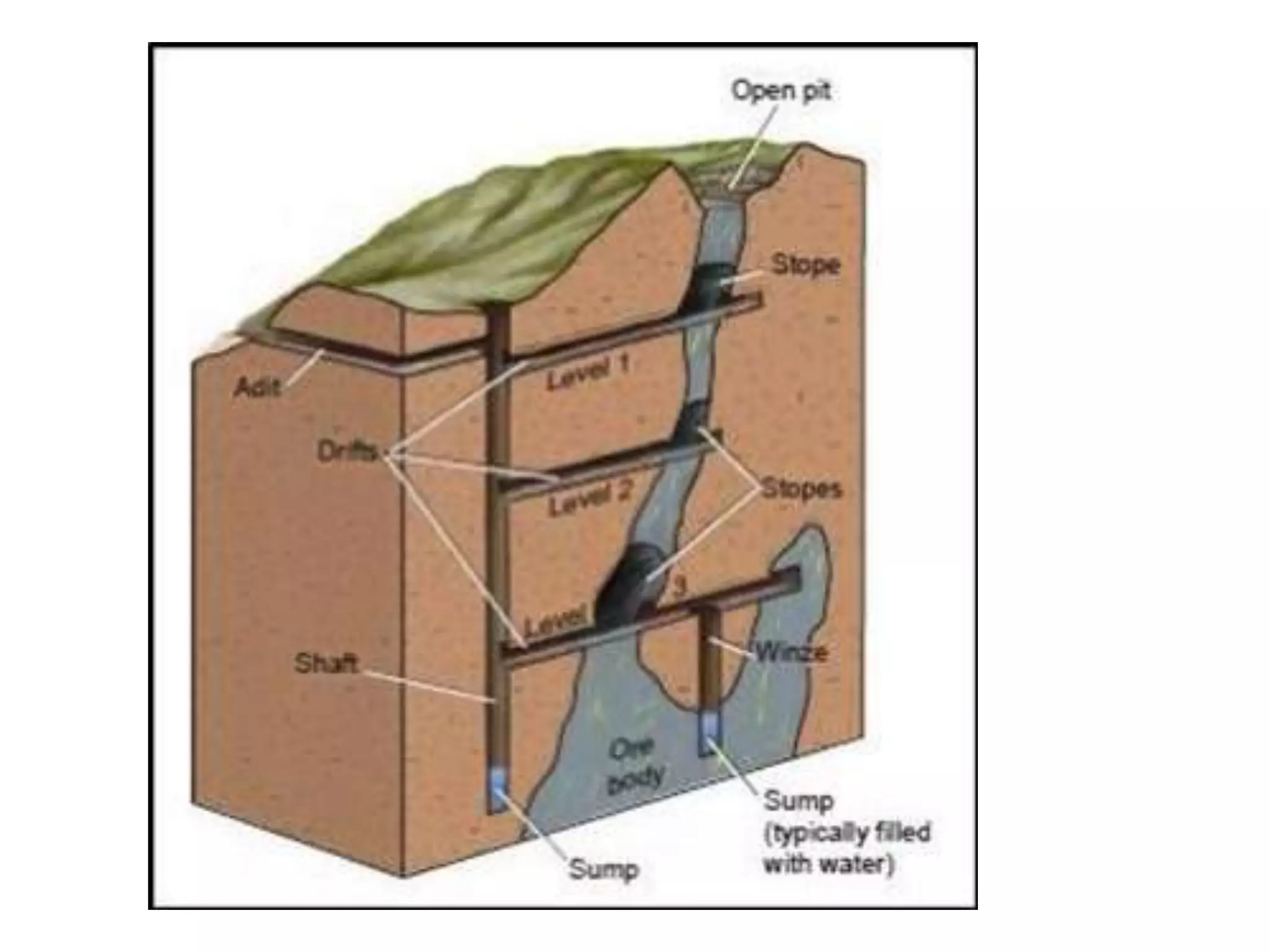
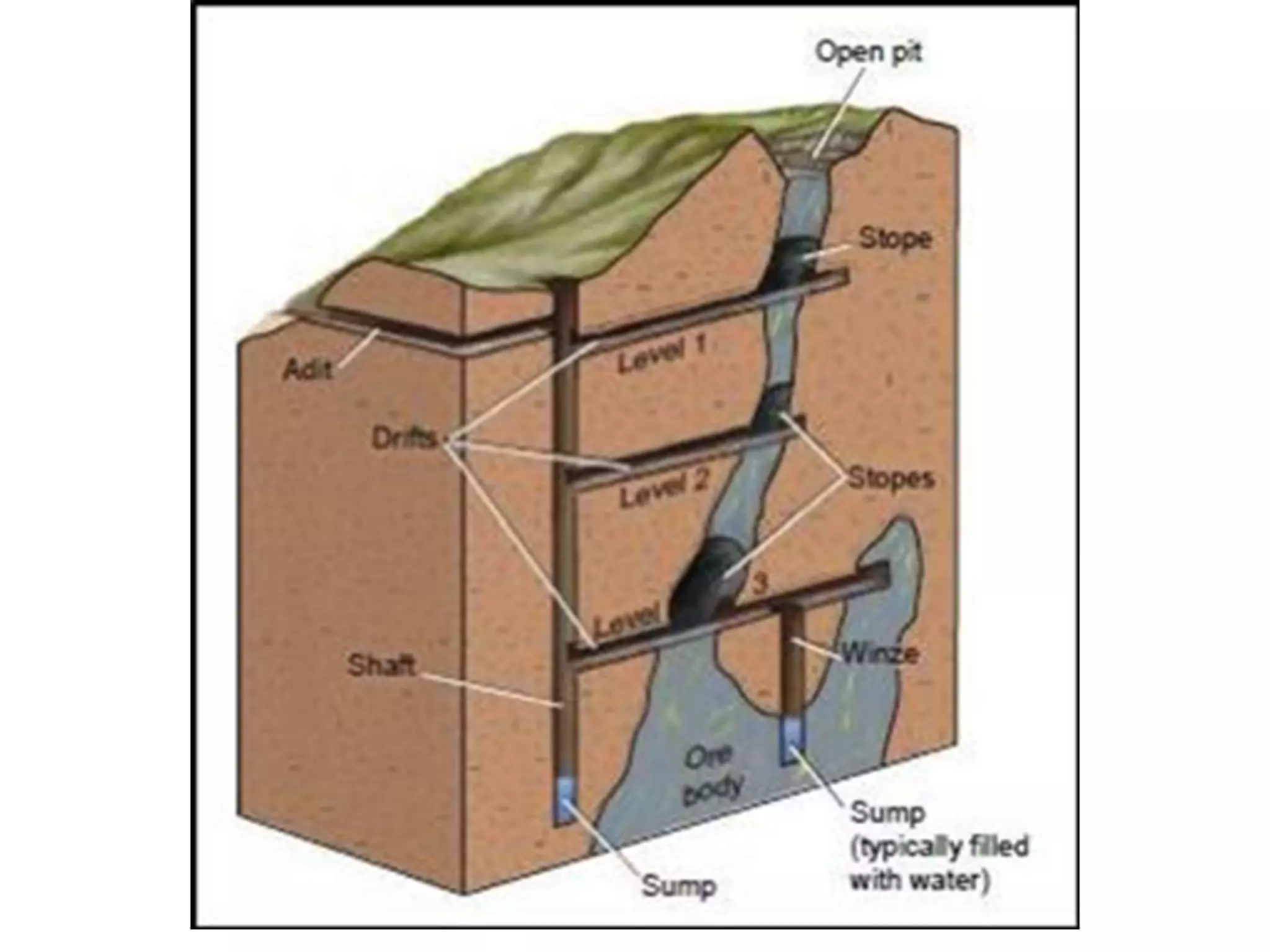
- Mining involves extracting valuable minerals from the earth through various surface and underground methods. Surface methods include strip mining, open-pit mining, mountaintop removal, and dredging. Underground methods involve excavating tunnels and shafts.
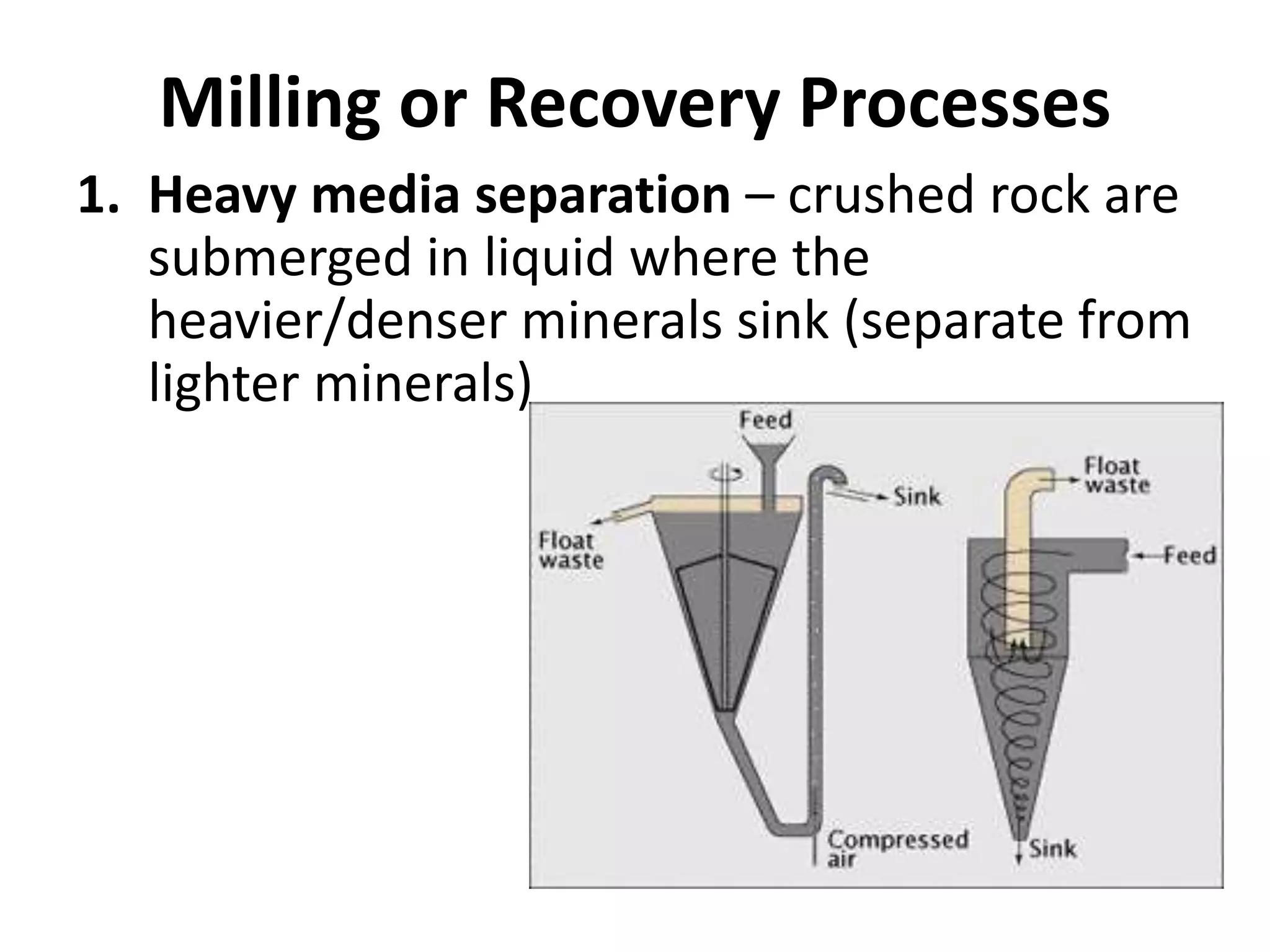
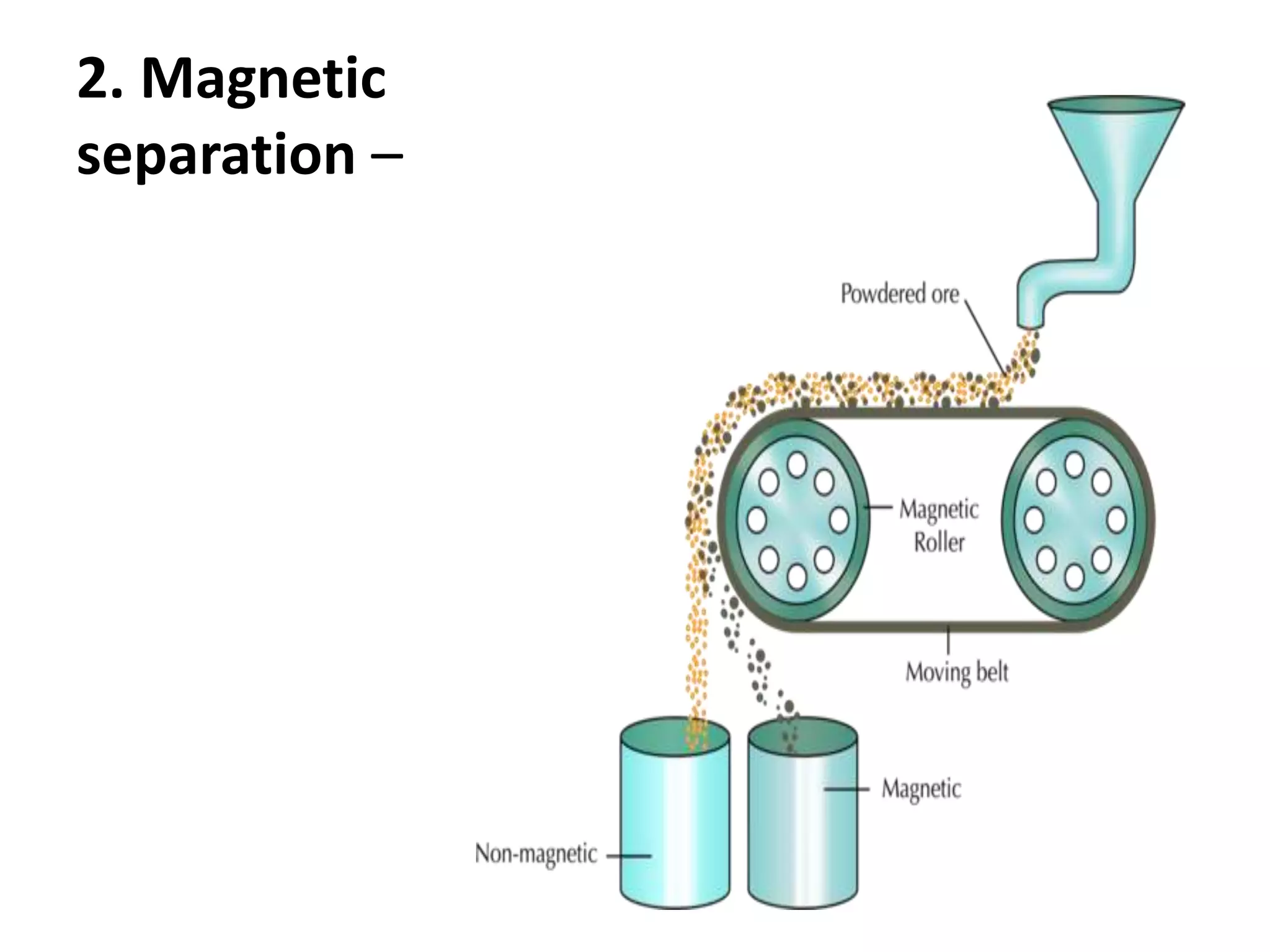
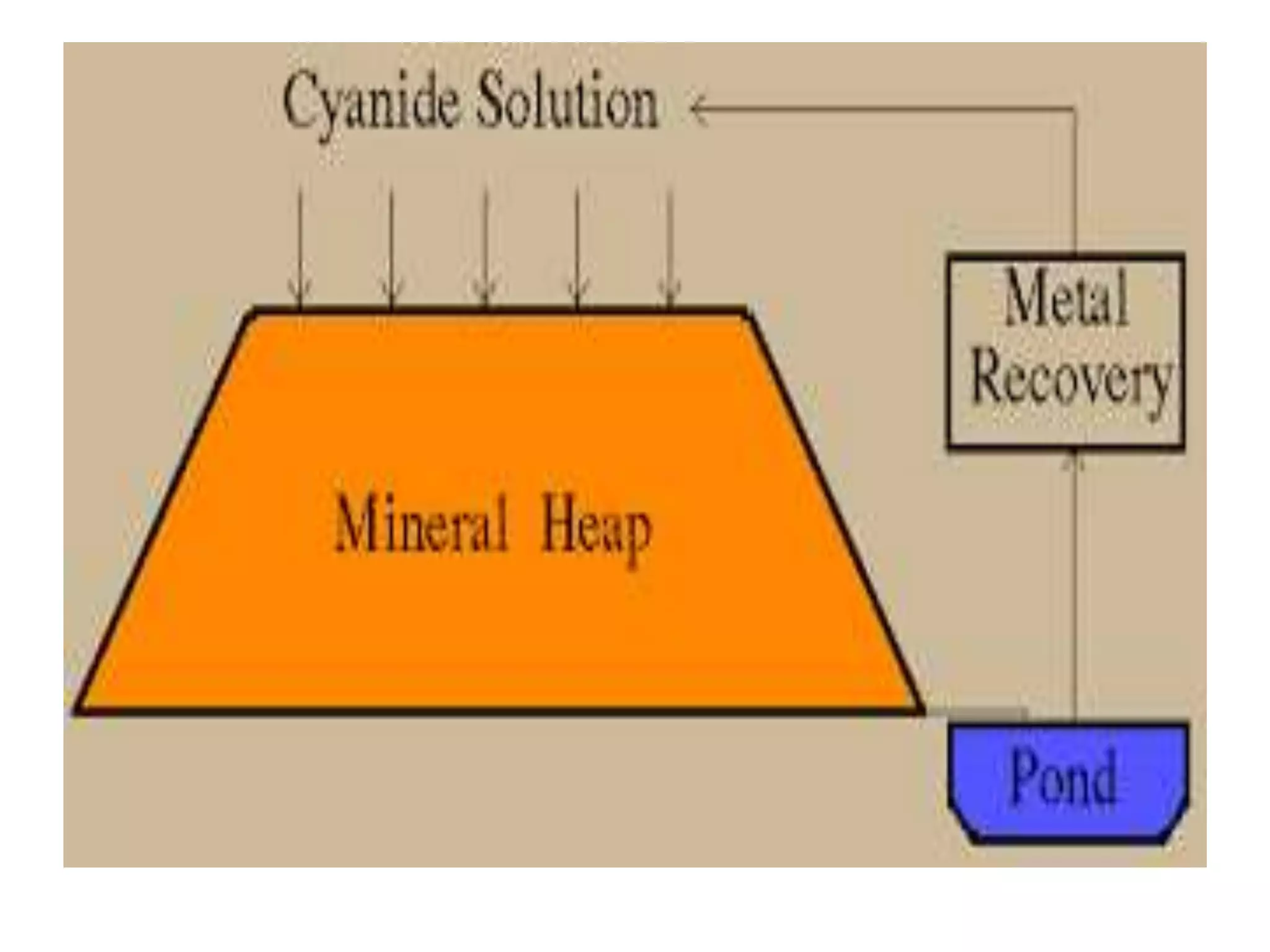
- The extraction process produces both ore and waste rock. Ore undergoes crushing, grinding, and separation processes like flotation and cyanidation to extract minerals.
- Mining has environmental impacts like flooding, erosion, water and air pollution, and wildlife habitat damage. Preventive measures include replanting vegetation and stabilizing slopes. The government regulates mining through agencies like MGB and EMB and laws like the Mining Act.