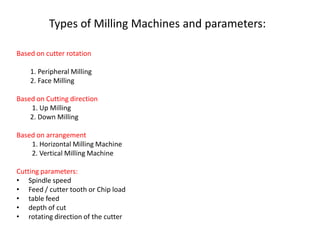
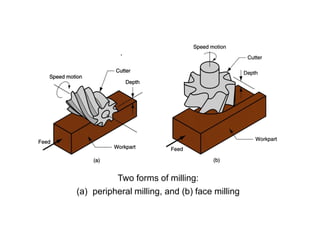
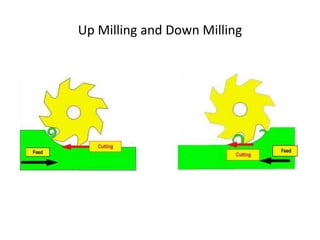
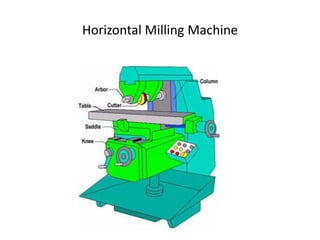
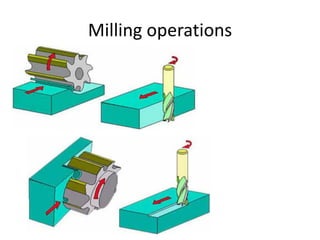
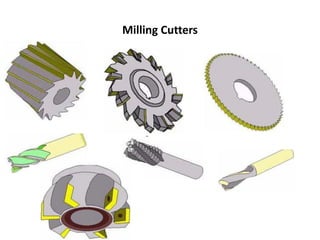
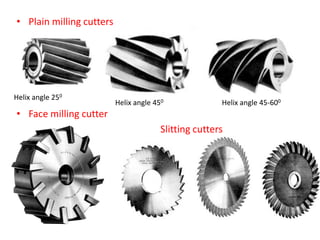
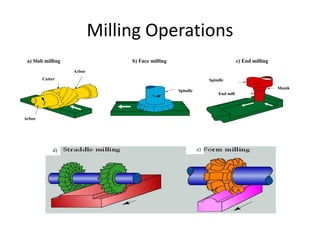
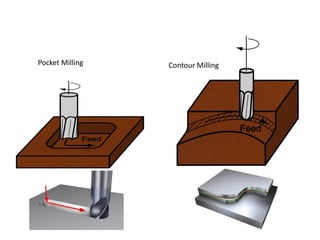
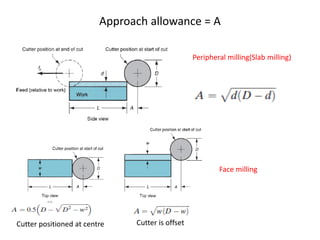
The document discusses milling processes and milling machines. It describes milling as a metal removal process that uses a rotating cutter with multiple teeth. There are different types of milling machines based on factors like the cutter rotation (peripheral, face), cutting direction (up, down), and arrangement (horizontal, vertical). Key cutting parameters in milling include spindle speed, feed rate, depth of cut, and rotating direction of the cutter. The main difference between peripheral and face milling is that peripheral milling involves a cutter axis parallel to the workpiece surface, while face milling involves a cutter axis perpendicular to the surface.