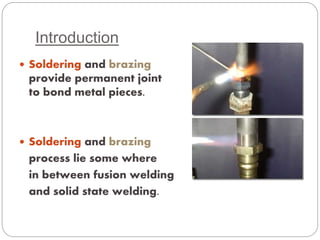
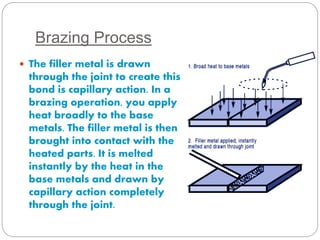
Soldering and brazing are metal joining processes where a filler metal is melted and drawn between closely fitted metal pieces through capillary action to form a permanent bond. Brazing differs from soldering in that the filler metal has a higher melting point above 450°C, while soldering uses filler metals with lower melting points. Common brazing methods include torch, furnace, dip, and induction brazing, while soldering is typically done with an iron or through wave soldering of printed circuit boards. Brazing and soldering offer advantages over welding like joining dissimilar metals, lower temperatures, less distortion and damage, and faster joining.