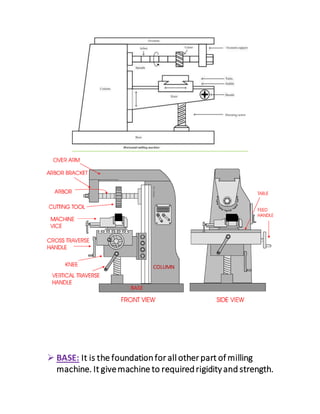
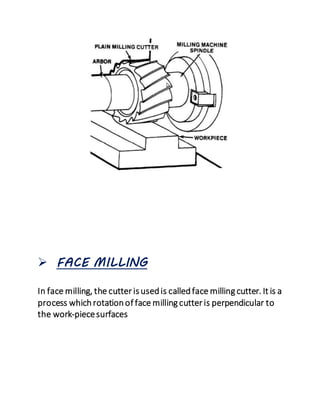
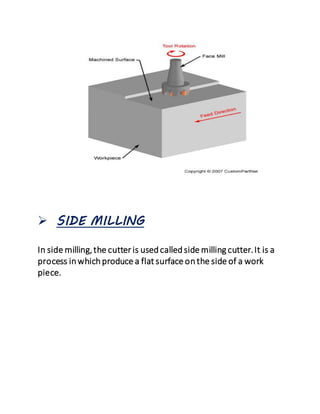
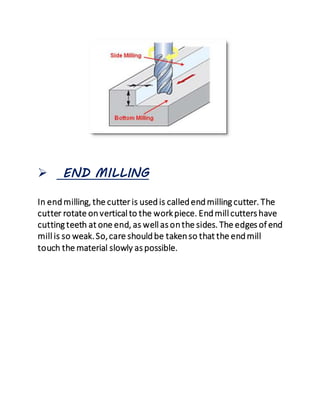
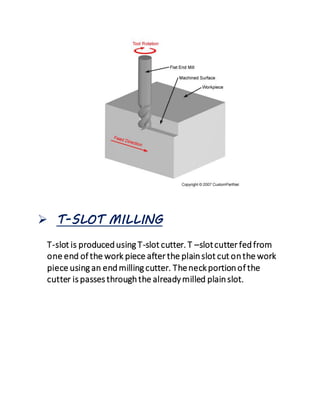
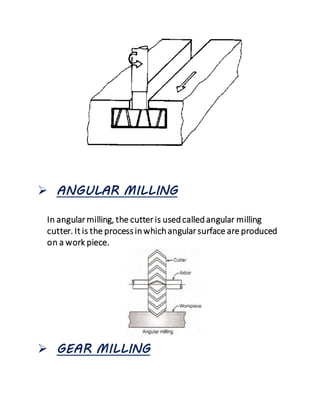
The document provides an overview of milling machines, which are used for metal removal through various milling operations such as slab, face, side, end, T-slot, angular, and gear milling. It classifies milling machines into horizontal and vertical types and explains the components and functions of each part, along with the difference between up milling and down milling. It concludes with references for further reading and is submitted by a student in mechanical engineering.