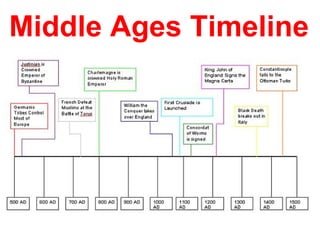
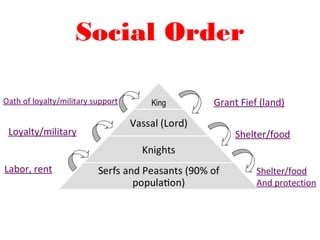
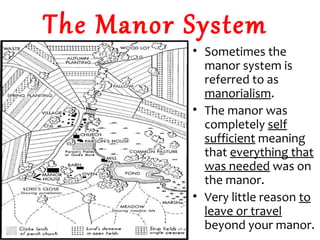
After the fall of Rome, Western Europe entered a period known as the Middle Ages from 400-1400 AD. During this time, there was a lack of central government and a rise in the power of the Catholic Church. A feudal system emerged to provide order and protection with serfs bound to the land. Society was stratified with one's social position determined by birth. The self-sufficient manorial system further isolated peasants to their manors with little reason to travel beyond.