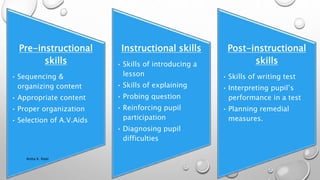
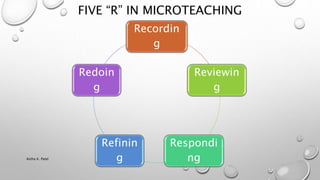
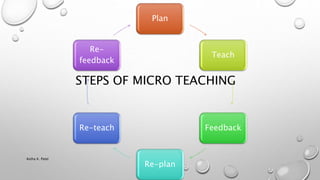
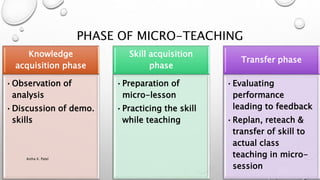
Microteaching is a teacher training technique that allows trainees to teach short lessons (5-20 minutes) to small groups of students (5-10) to develop their teaching skills. The lessons are videotaped and the trainees receive feedback to improve. It focuses on individual teaching skills like lesson introduction, explanation, questioning, and student engagement. The process involves planning, teaching, receiving feedback, re-planning, and re-teaching lessons to develop core pre-instructional, instructional, and post-instructional skills needed for effective teaching.