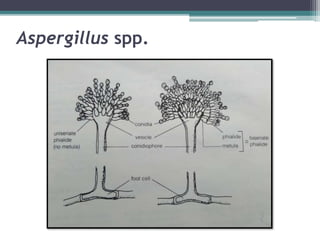
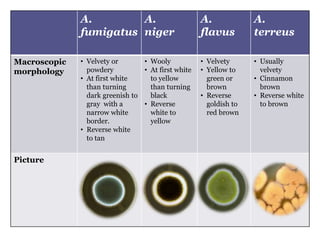
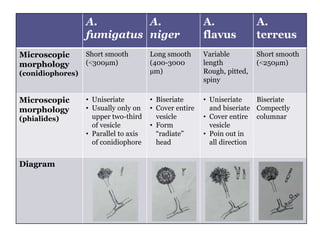
This document describes the genus Aspergillus. It discusses the typical growth rate of Aspergillus species, with most growing rapidly and maturing within 3 days, though some species are slower. It also describes the common colonial and microscopic morphologies seen in Aspergillus, including velvety or cottony surface textures, septate hyphae, conidiophores, vesicles, and phialides that produce chains of conidia. Specific details are provided for several common Aspergillus species.