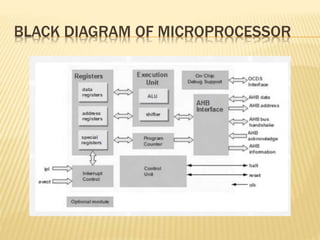
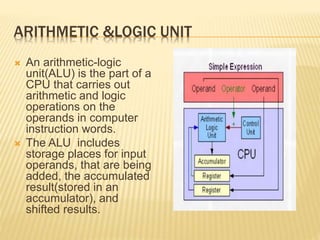
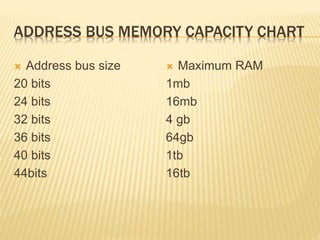
The document provides an overview of microprocessor organization. It discusses that a microprocessor functions as the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer, providing computational control. It has different components like the CPU, I/O, buses, control unit, registers, cache memory, and ALU. The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on given data by reading instructions one at a time and performing the specified data manipulation. Necessary tools for a microprocessor include the CPU, I/O, address and data buses, control unit, special and general purpose registers, L1 and L2 cache memory, and buses.