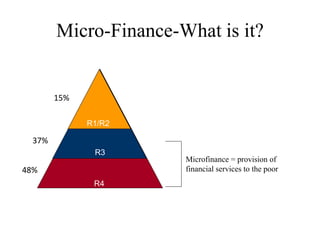
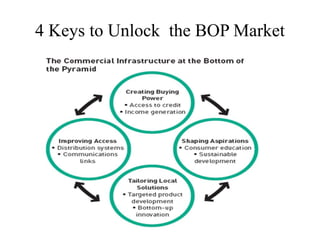
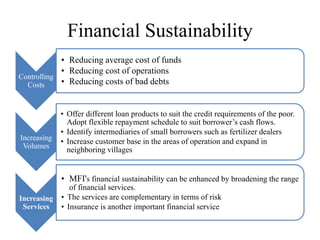
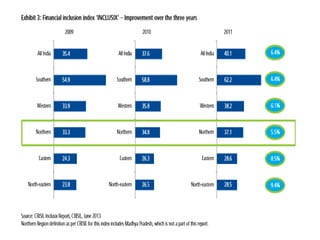
Microfinance aims to provide financial services to low-income populations. In India, microfinance reaches over 33% of the population through self-help groups (SHGs) and microfinance institutions (MFIs). SHGs help empower the poor through collective decision making and access to banking. MFIs face challenges including high operating costs due to low-value transactions, and a lack of trained talent and infrastructure. Financial inclusion efforts in India are focusing on new banking licenses, mobile payments, ATM rollout, and using Aadhaar identification to expand access to financial services. Recommendations include incentivizing mainstream banks to enter microfinance and building community-based financial institutions.