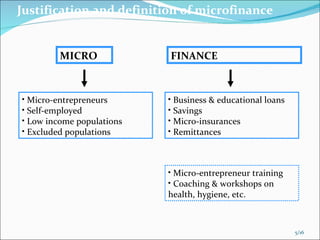
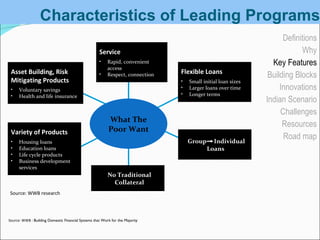
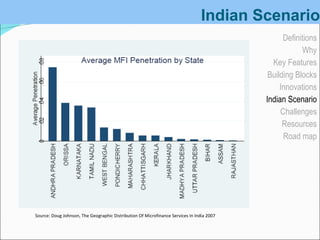
Microfinance involves providing small loans, savings opportunities, and other basic financial services to low-income individuals. It began in the 1970s with programs lending small amounts to groups of poor women. In India, microfinance has existed informally for ages and various government initiatives over time helped establish a legal framework and institutions to support it, such as cooperative banks and NABARD. Today, around 60% of microfinance institutions in India are registered as societies and most use the self-help group model to deliver services to over 100 million poor households.