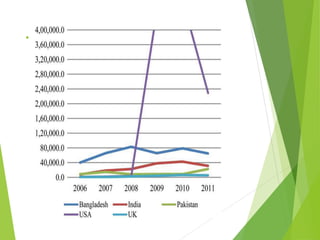
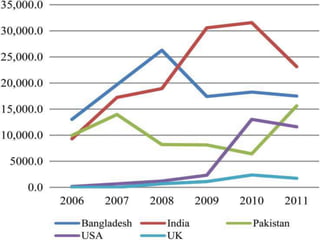
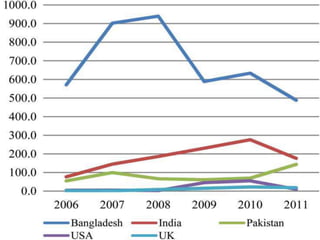
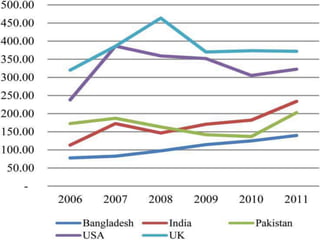
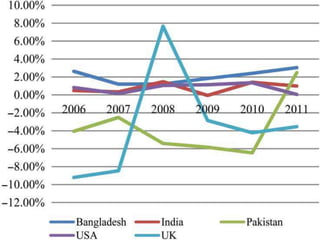
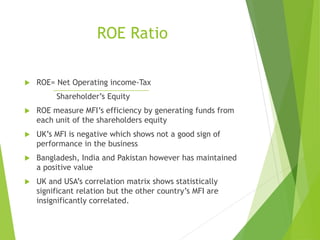
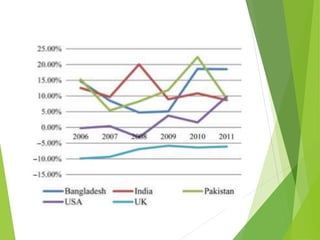
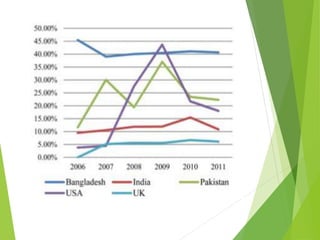
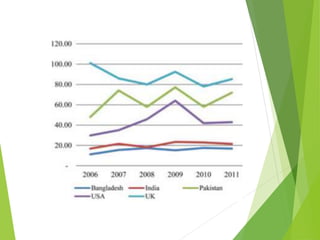
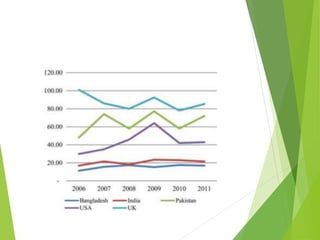
This study analyzes microfinance institutions (MFIs) in three Asian developing countries (Bangladesh, Pakistan, India) and two developed economies (UK, USA) to assess their effectiveness in reducing poverty. Findings indicate that Bangladesh and India excel in microfinance implementation, while MFIs in developed countries show unsatisfactory performance and a need for greater awareness. The research highlights significant correlations between MFIs' performance metrics, indicating varying levels of success across the studied nations.