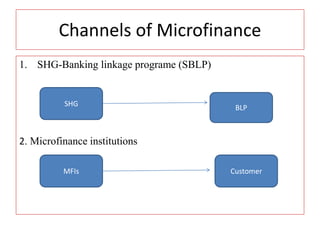
Microfinance provides small, short-term loans, savings, insurance, and training opportunities to low-income groups without requiring collateral. Microfinance has existed informally for ages in India but legal frameworks and institutions like cooperatives, regional rural banks, NABARD, and microfinance institutions (MFIs) have expanded access. Currently, only 14% of the 32 crore Indians living below the poverty line have access to microfinance. Issues facing MFIs include high interest rates, over-lending, multiple borrowing, and coercive practices. Recent regulations have aimed to address these issues and expand microfinance's role in poverty alleviation.