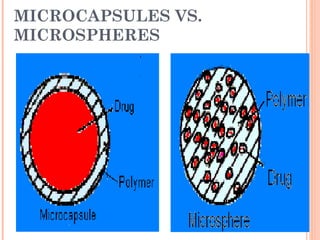
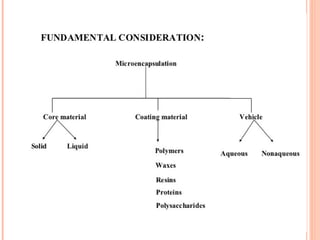
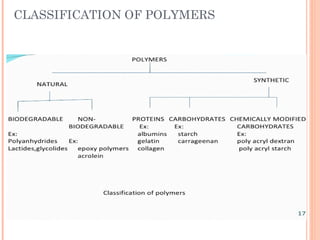
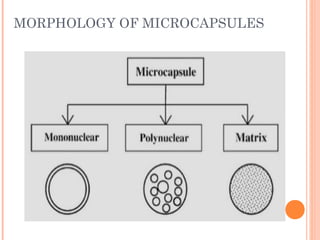
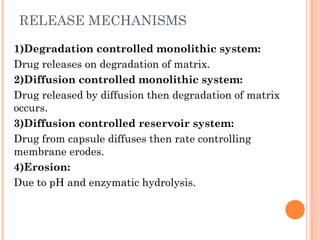
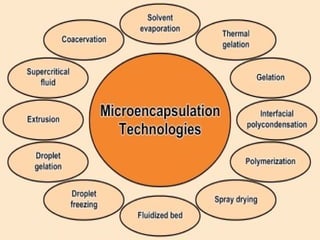
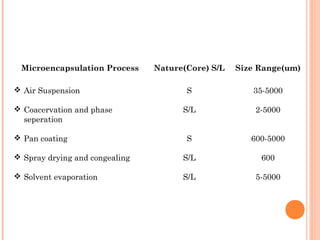
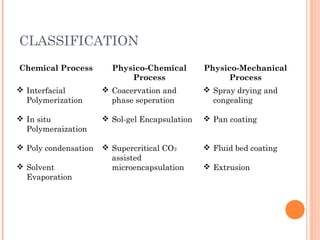
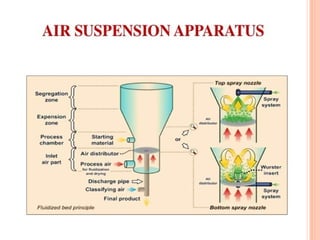
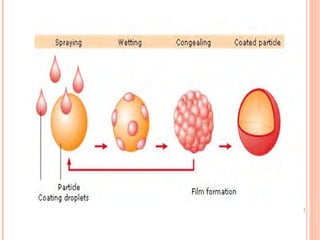
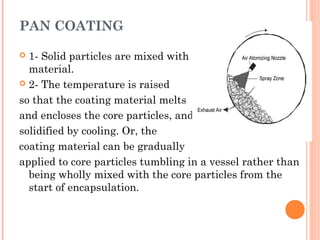
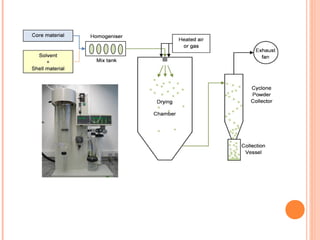
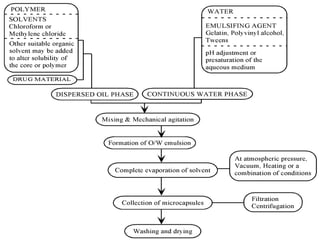
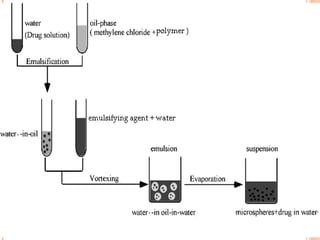
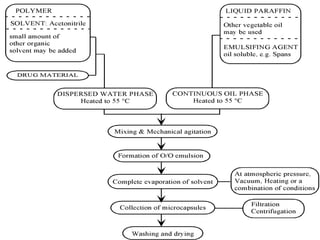
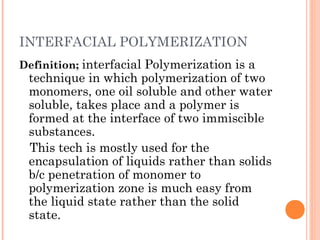
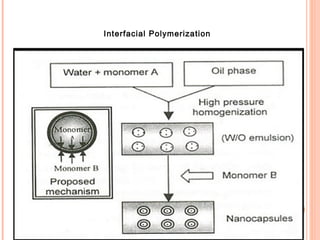
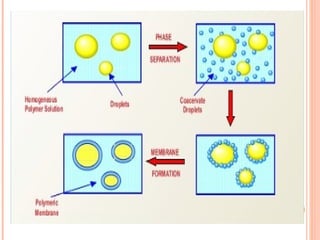
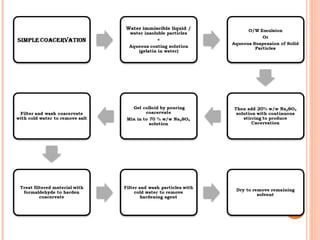
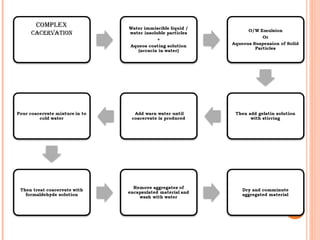
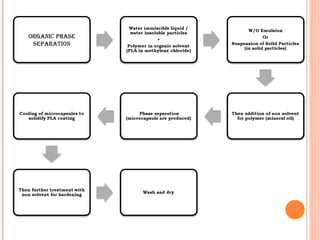
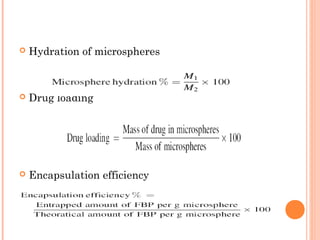
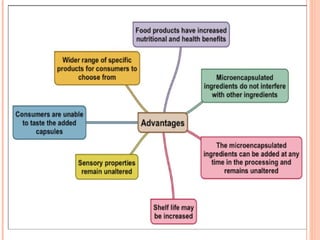
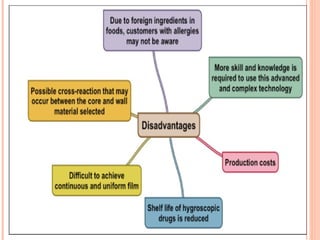
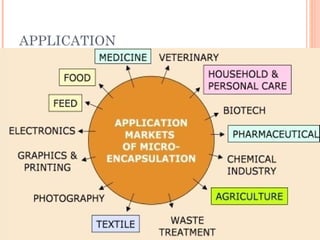
This document provides an overview of microencapsulation. It defines microencapsulation as coating solid, liquid, or gas core materials that are 5-5000 μm in size. Reasons for microencapsulation include sustained release, taste/odor masking, separating incompatible materials, and protecting materials from environmental conditions. Key considerations are the core and coating materials and the release characteristics. Common techniques include solvent evaporation, spray drying, pan coating, and interfacial polymerization. Microencapsulation has various applications and advantages such as converting liquids to powders and preventing gastric irritation, but also has disadvantages like potential toxicity.