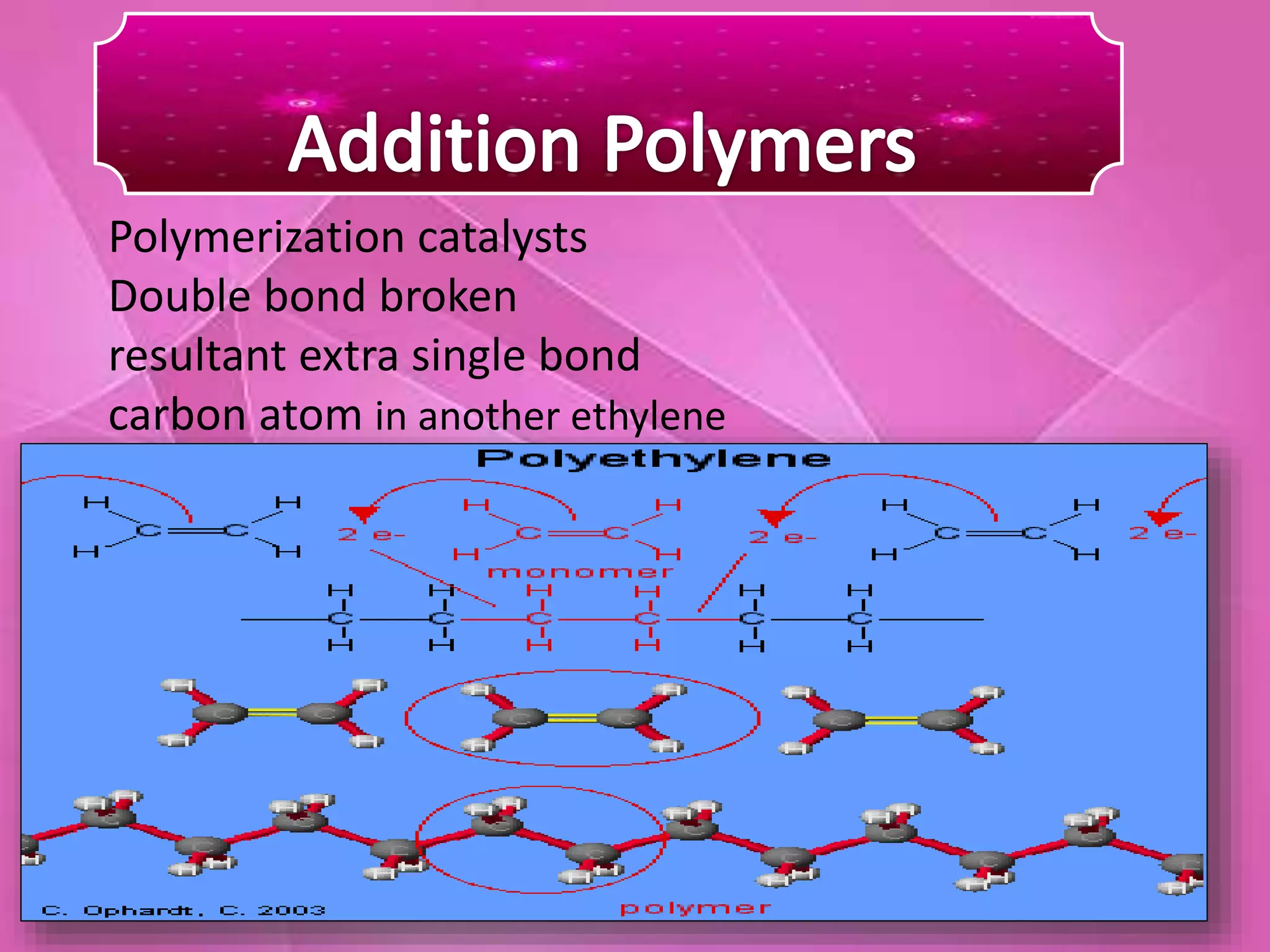
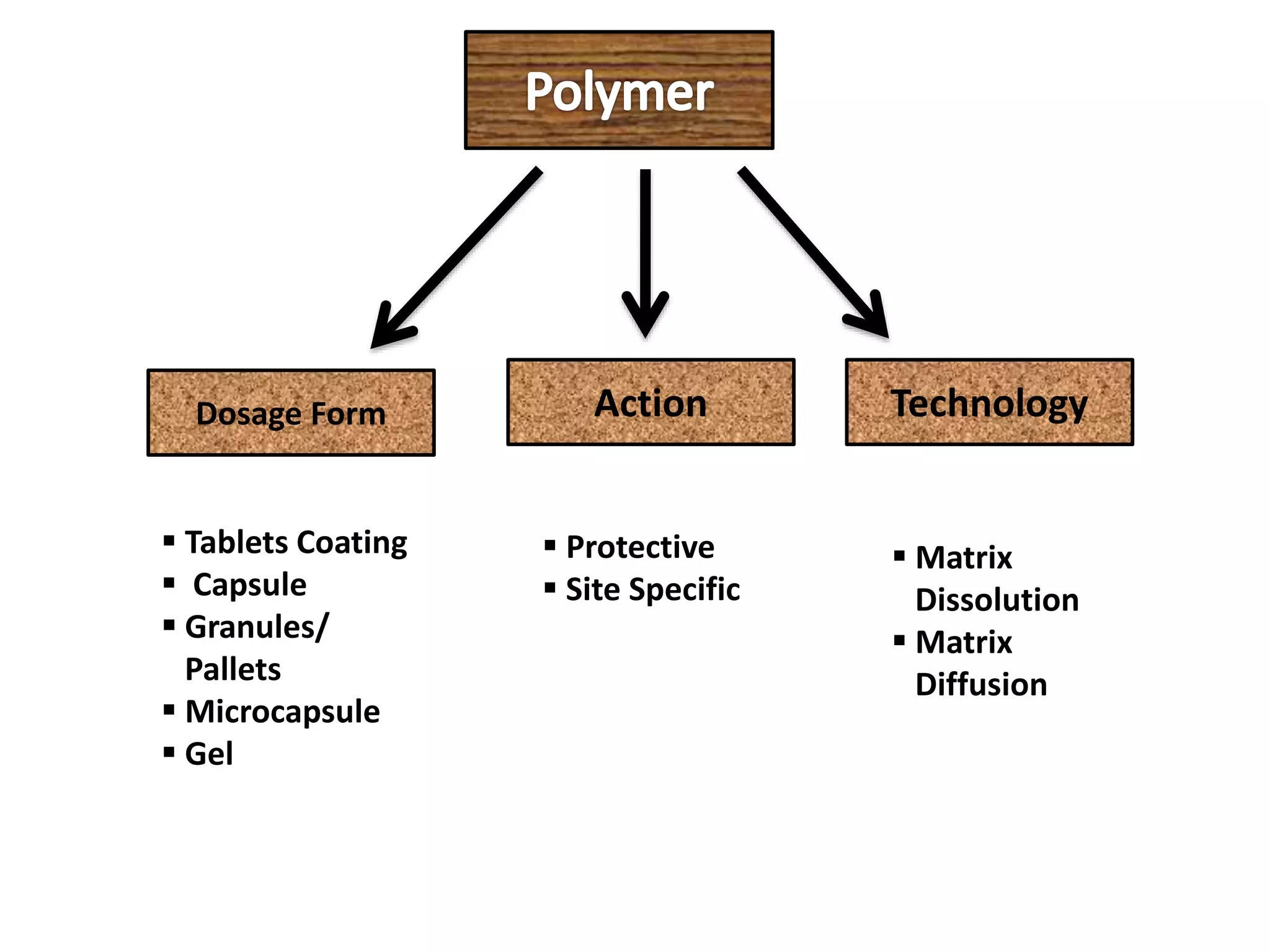
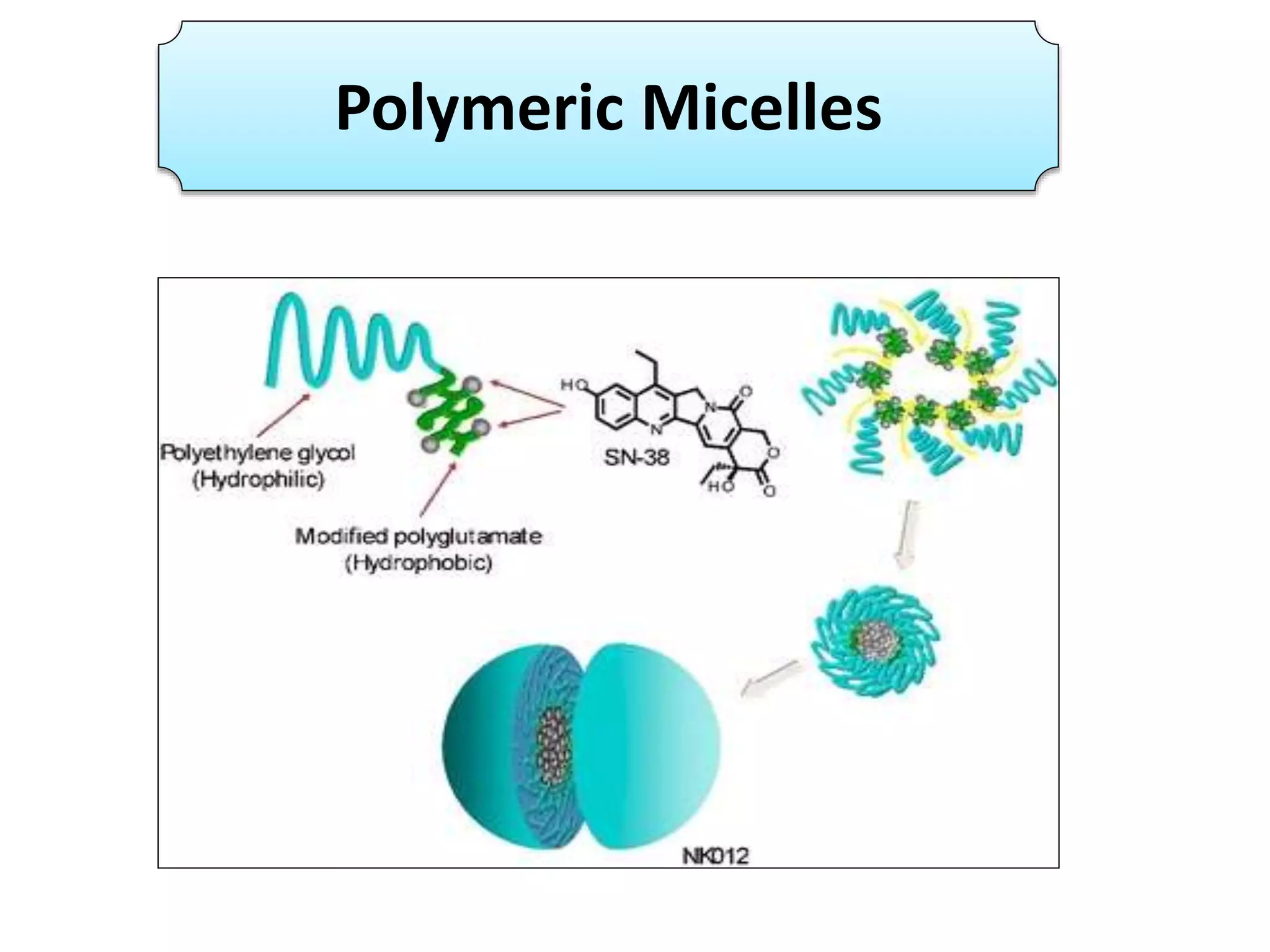
This document discusses various polymer-based drug delivery technologies, including hydrogels for controlled drug delivery and polymeric micelles. It provides information on what polymers are, how they are constructed, and examples of natural and synthetic polymers. It then describes different polymer technologies for modifying drug release profiles from formulations, such as film coatings, capsules, microcapsules, gels, and matrix systems that release drugs through dissolution, diffusion, or degradation. Specific technologies like hydrogels, pulsincaps, and ringcap systems are explained. In conclusion, polymer drug delivery is seen as having great potential for mimicking natural products and further development requires extensive safety testing.