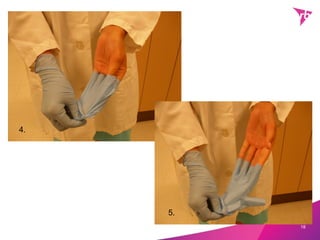
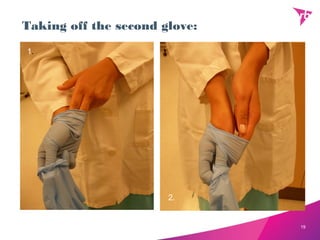
The document provides an overview of quality control procedures related to microbiology and hand hygiene. It discusses the importance of hand hygiene in reducing pathogen transmission, proper hand washing and sanitization techniques, and highlights frequently missed areas. It also describes finger dab testing procedures conducted every six months to monitor bacterial levels on personnel and ensure standards are met. Personnel hygiene policies regarding illness, clothing, and health examinations are outlined to maintain cleanliness. Demonstrations of proper glove removal and disposal techniques conclude the document.