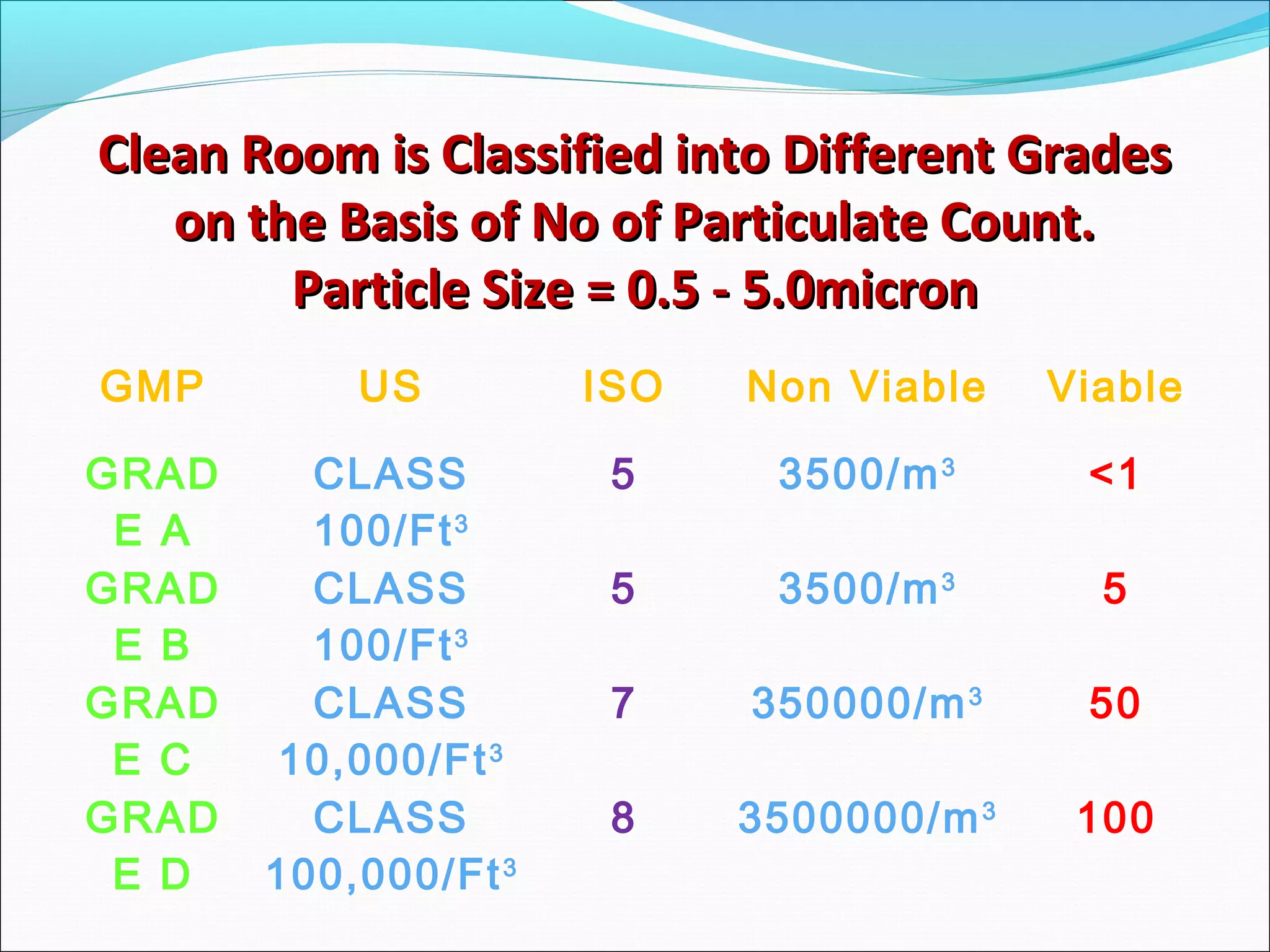
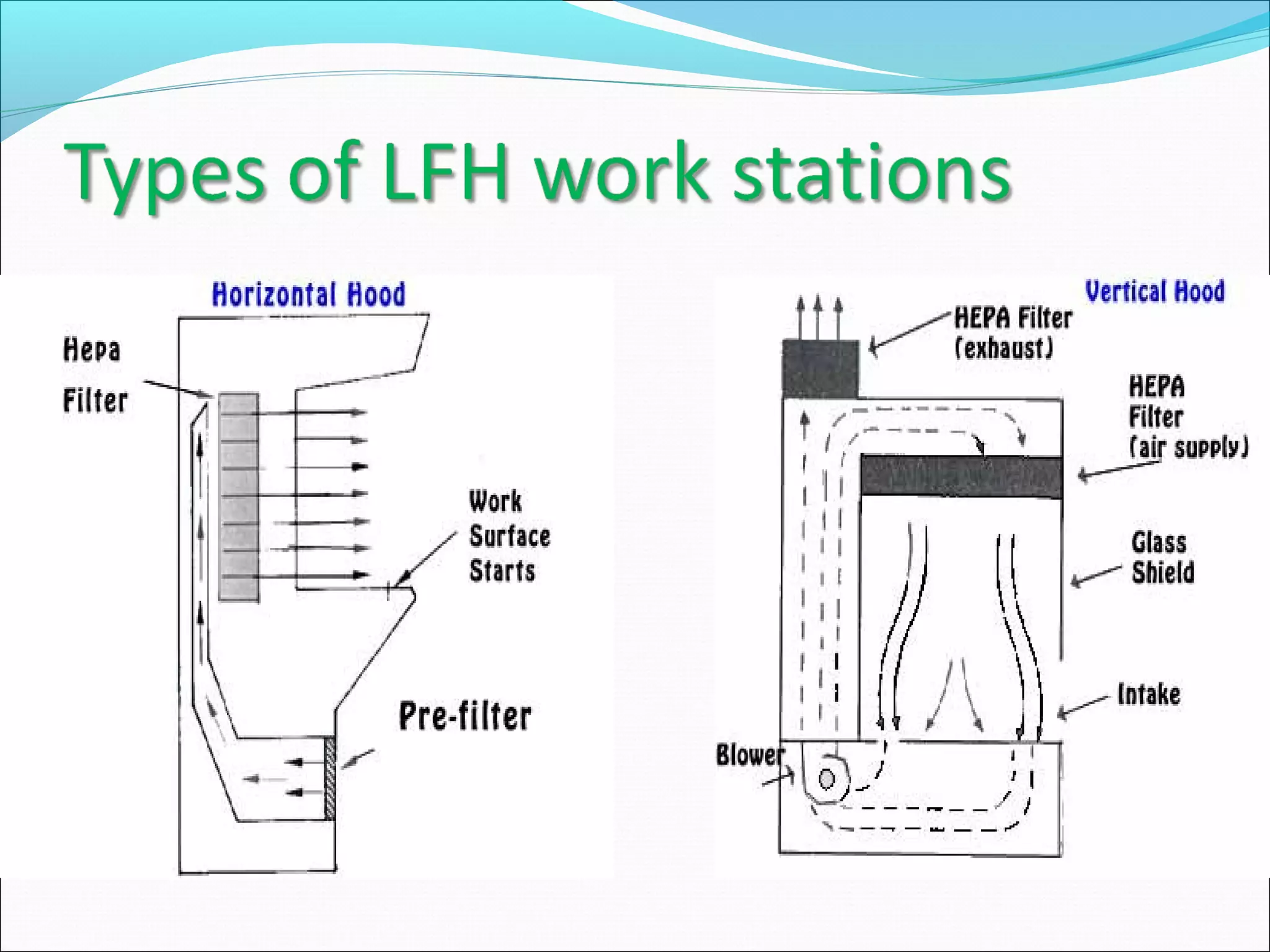
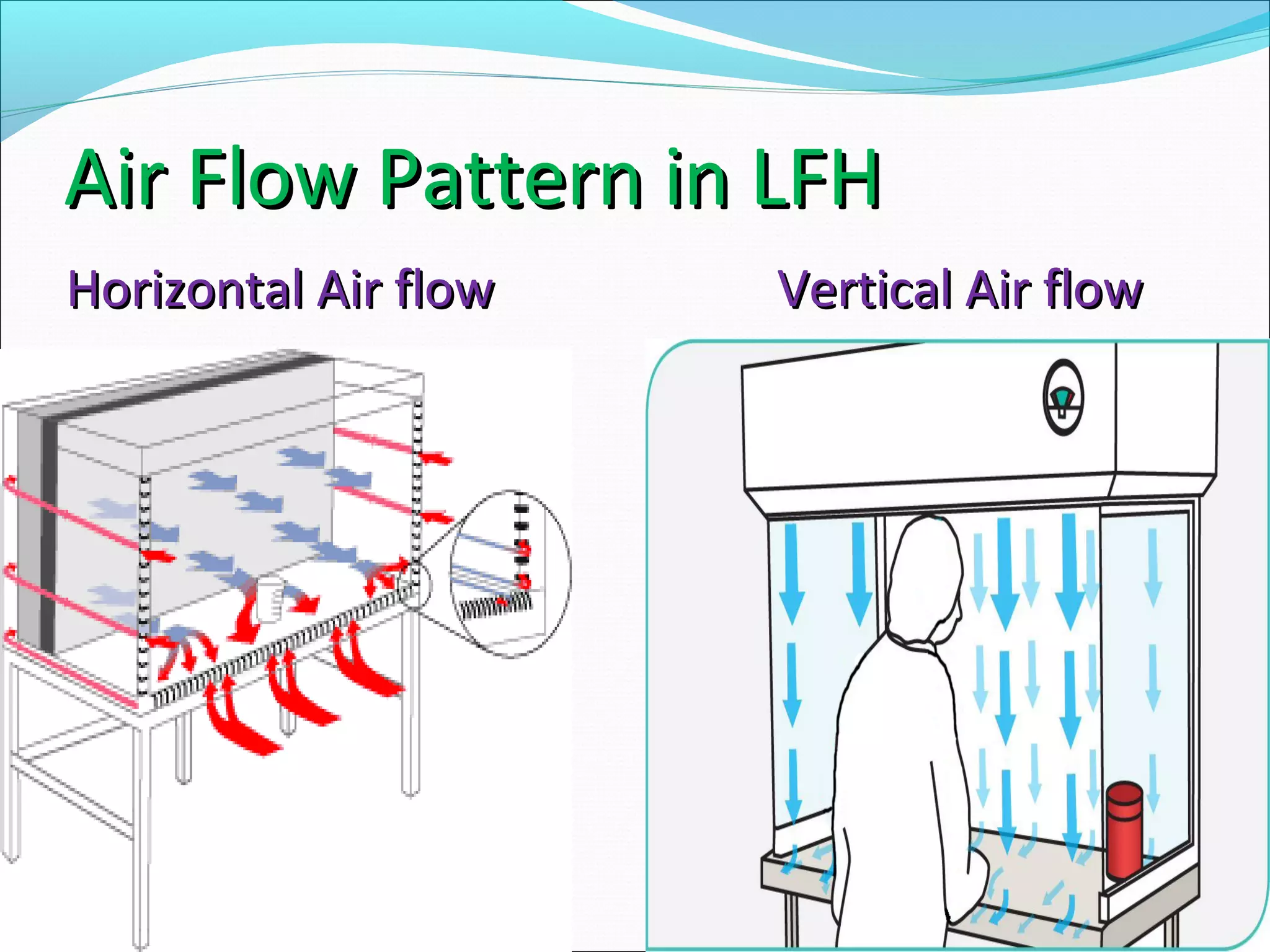
The document discusses aseptic filling techniques used to minimize contamination during manufacturing of sterile drug products. It outlines three main areas of control: environmental control through clean rooms and HVAC systems, equipment control using sterilization and sanitization, and individual control with personnel hygiene and gowning. Key aspects covered include clean room classification, HEPA filters, air locks, laminar flow hoods, sterilization methods, and environmental monitoring to ensure an aseptic environment is maintained.