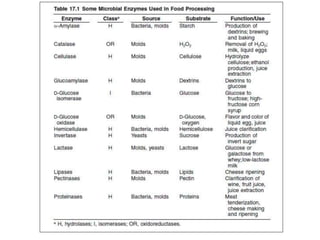
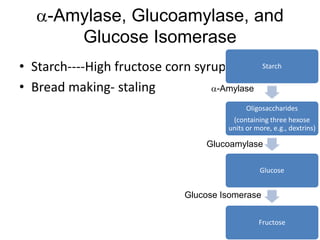
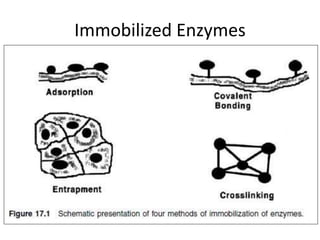
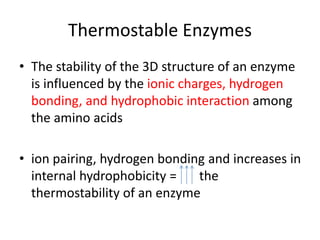
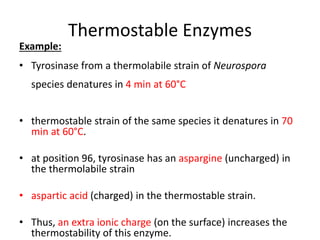
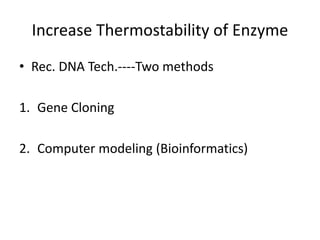
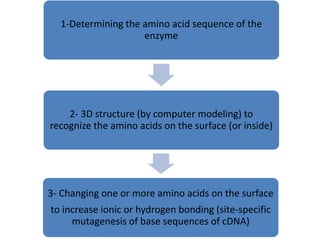
Microbial enzymes have several advantages for food processing including producing specific products through single step reactions and allowing control over reactions. Common enzymes used include amylases, catalase, cellulases, invertase, lactase, lipases, and proteases. Recombinant DNA technology has improved enzyme efficiency by allowing production in bacterial sources. Immobilized enzymes can be recycled but may have reduced activity. Thermostable enzymes are advantageous for food processing as they allow increased production rates and reduced contamination risks. Methods to improve enzyme thermostability include gene cloning and computer modeling to modify amino acid sequences. Enzymes can also help treat food waste by breaking down polysaccharides, proteins, and other materials for conversion to valuable products like