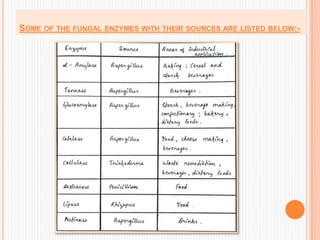
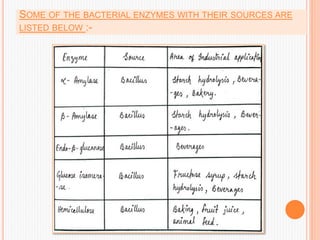
Microbial sources contribute about 80% of overall enzyme production, with fungi and bacteria being the dominant sources. Fungal enzymes like amylase and cellulase and bacterial enzymes like proteases are commonly used industrially. Enzymes are produced via fermentation using microbial strains improved through methods like mutagenesis. Fermentation allows for large-scale production of enzymes like α-amylase, lactase, and protease. Microbial sources are preferred over plants and animals for enzyme production due to easier extraction/purification and the ability to genetically engineer microbes for higher yields.