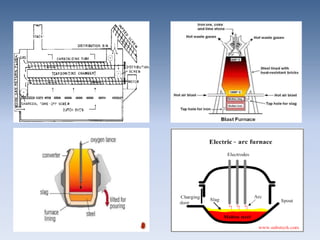
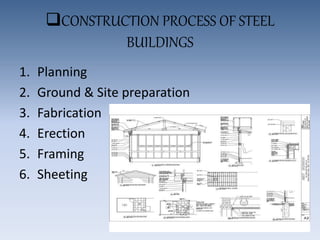
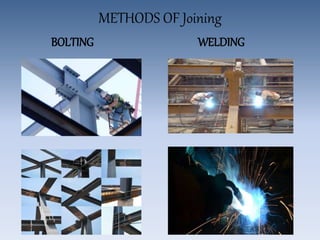
The document discusses the properties and manufacturing of steel, emphasizing its use in modern construction due to its strength, flexibility, and recyclability. It outlines the construction process of steel buildings, site investigations, and compares steel structures to concrete structures, noting both their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it highlights notable steel structures and relevant standards in the industry.