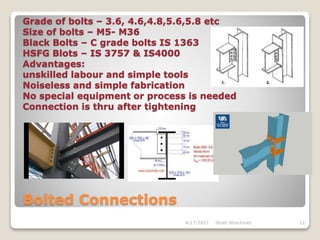
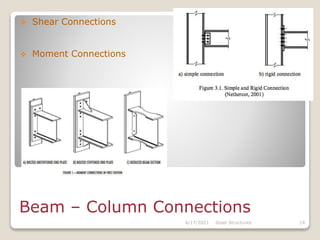
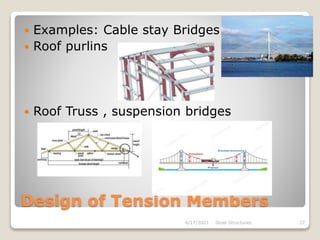
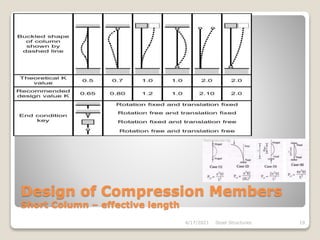
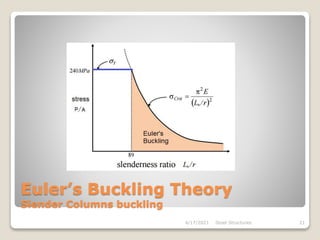
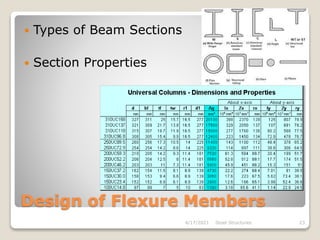
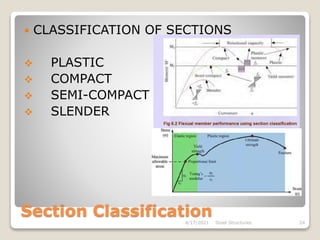
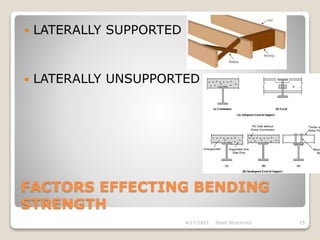
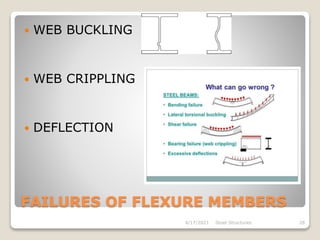
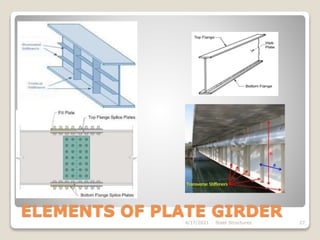
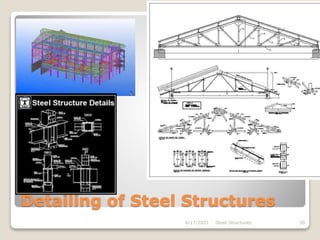
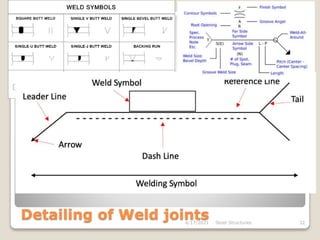
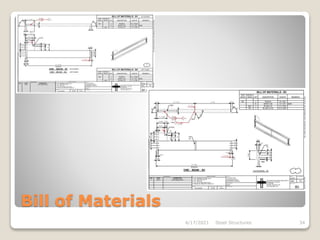
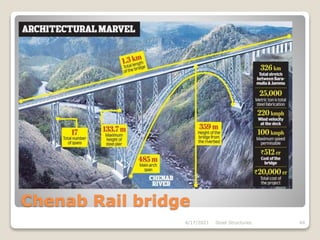
This document provides an overview of steel structures design and construction. It discusses materials and specifications, structural design considerations, common member types, connections, fabrication, erection, and detailing. The key points covered include load calculations, stress analysis, failure modes of tension, compression, and flexural members, and welding and bolted joint design. Methods for plate girder design and construction are also summarized.