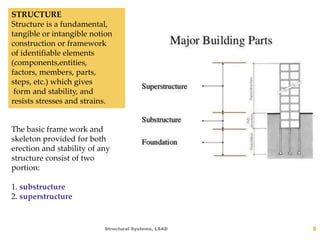
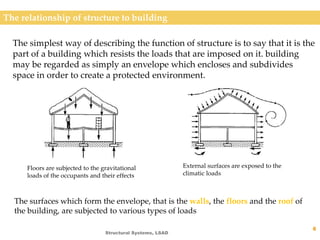
This document discusses different types of structural systems. It defines structure and explains that structures can be man-made or natural. Man-made structures are constructed by humans, while natural structures occur without human involvement. The document then discusses four main types of structural systems: section/bulk active systems using rigid elements to redirect forces through bending; vector active systems using tension and compression elements; form active systems relying on flexible elements and particular shapes; and surface active systems using planar elements under tension, compression or shear. Examples are provided for each type of structural system.