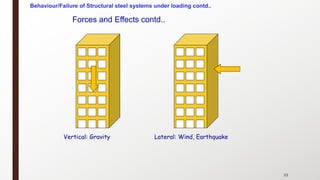
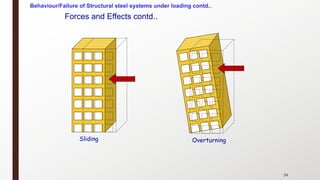
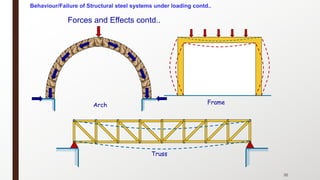
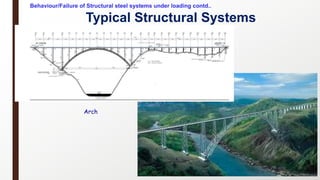
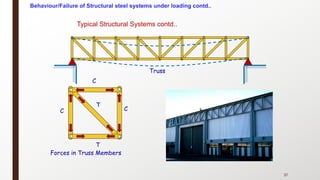
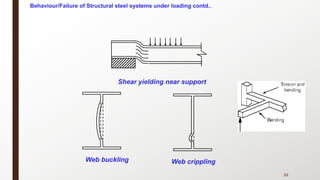
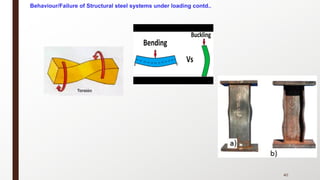
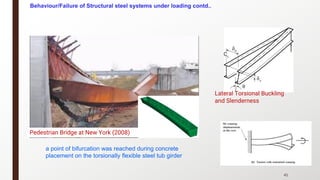
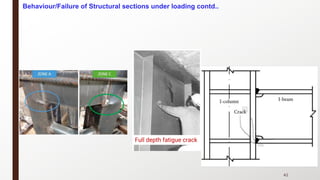
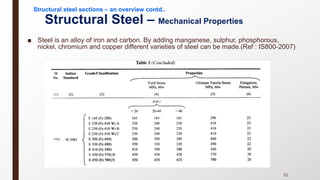
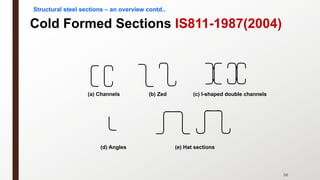
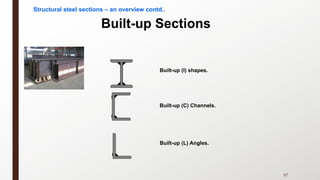
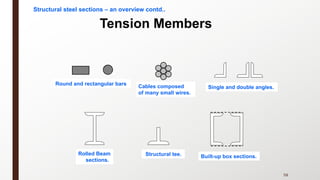
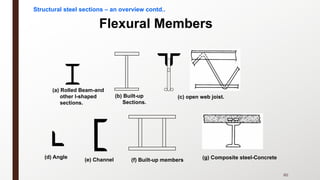
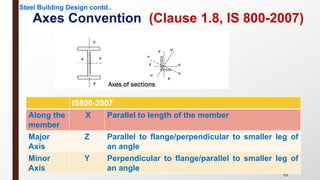
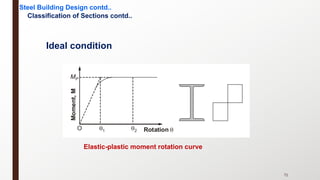
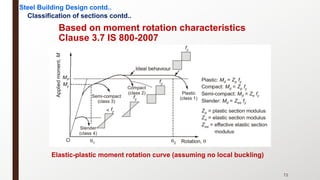
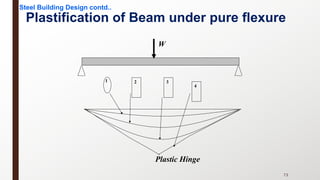
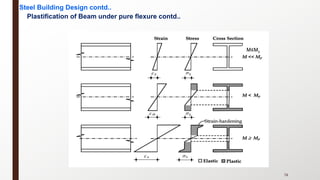
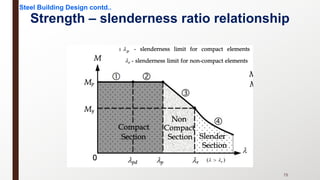
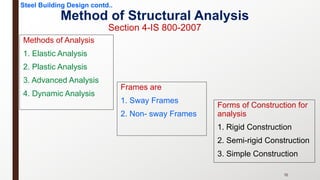
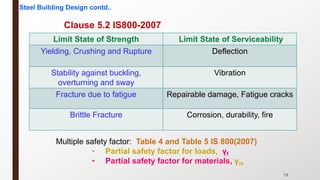
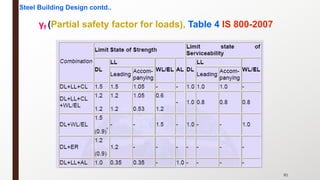
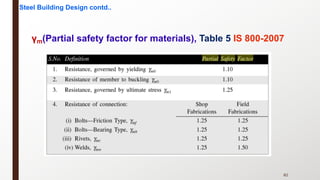
This document provides an overview of steel building design and structural steel systems. It discusses the characteristics of structural steel, popular steel structures, advantages of steel structures, and how steel structures behave under loading. It also covers structural steel sections, failures of steel structures, and choices in structural systems for steel buildings, including framework/skeletal and shell systems.