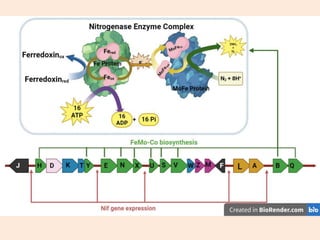
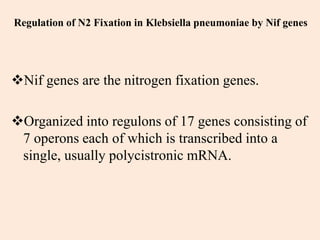
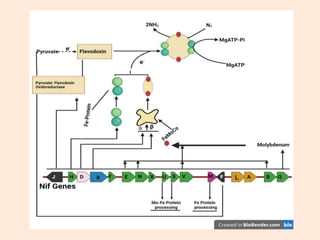
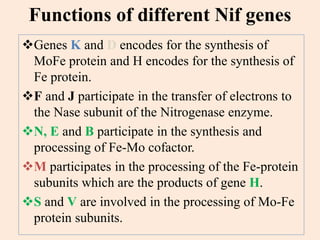
Nitrogenase enzyme is crucial for nitrogen fixation, found in bacteria associated with plant roots like legumes, consisting of large and small protein subunits that require Mg2+ ions for activation. Nif genes are responsible for regulating nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae, comprising 17 genes organized into operons that encode various functions related to the synthesis and processing of the nitrogenase components. Gene expression is regulated by external and internal systems, with the ntr system activating nif genes in response to nitrogen starvation.