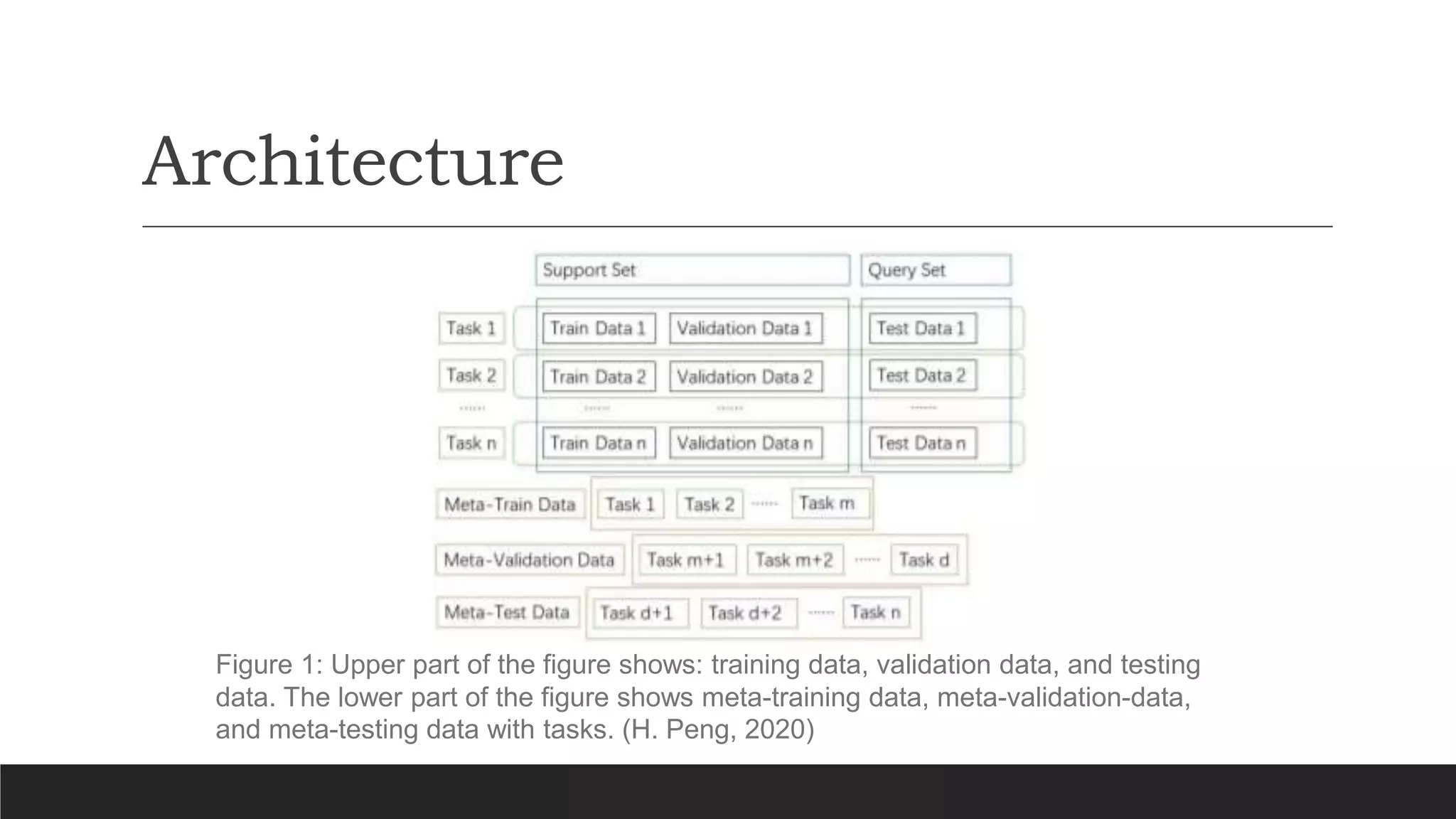
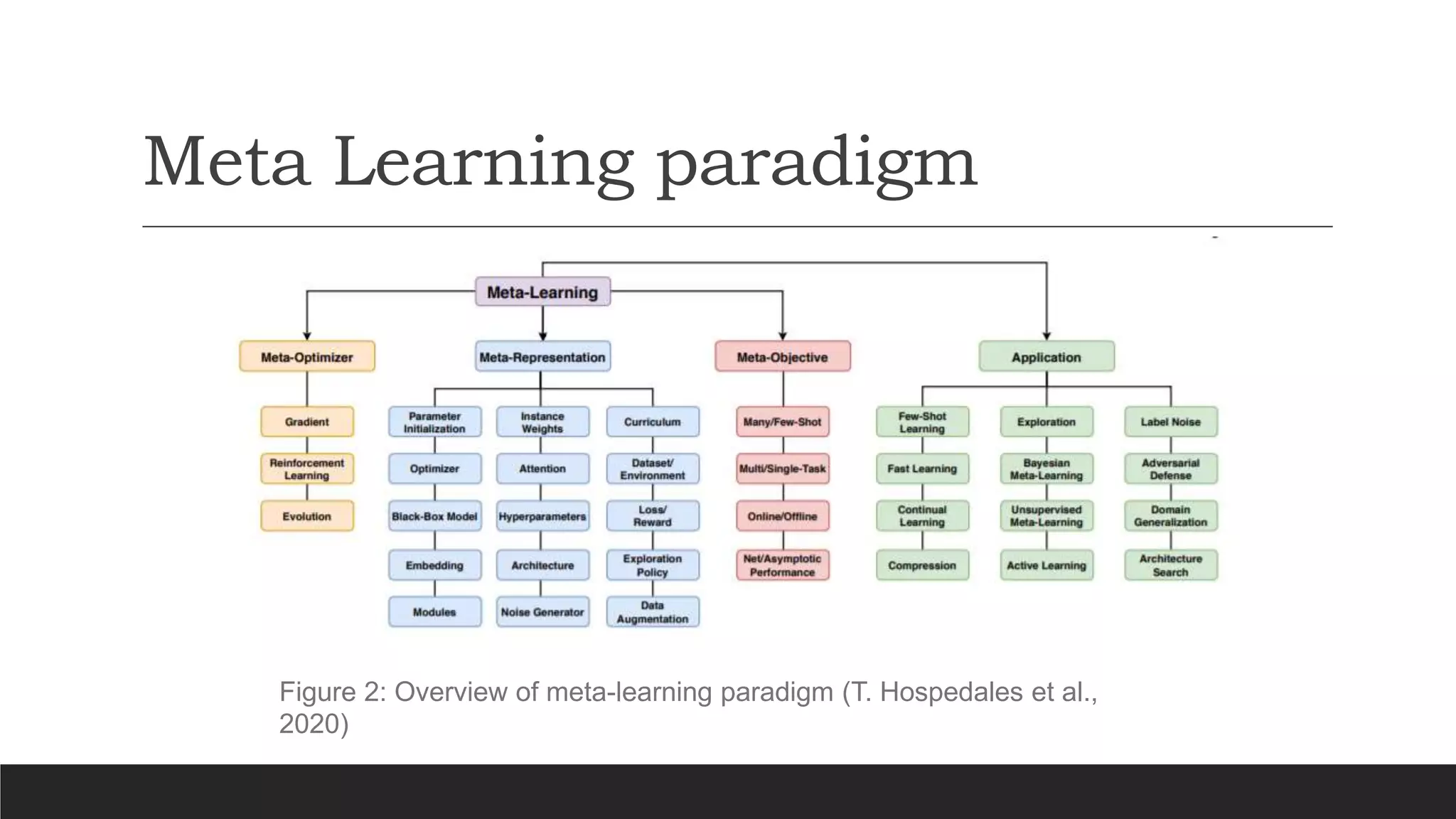
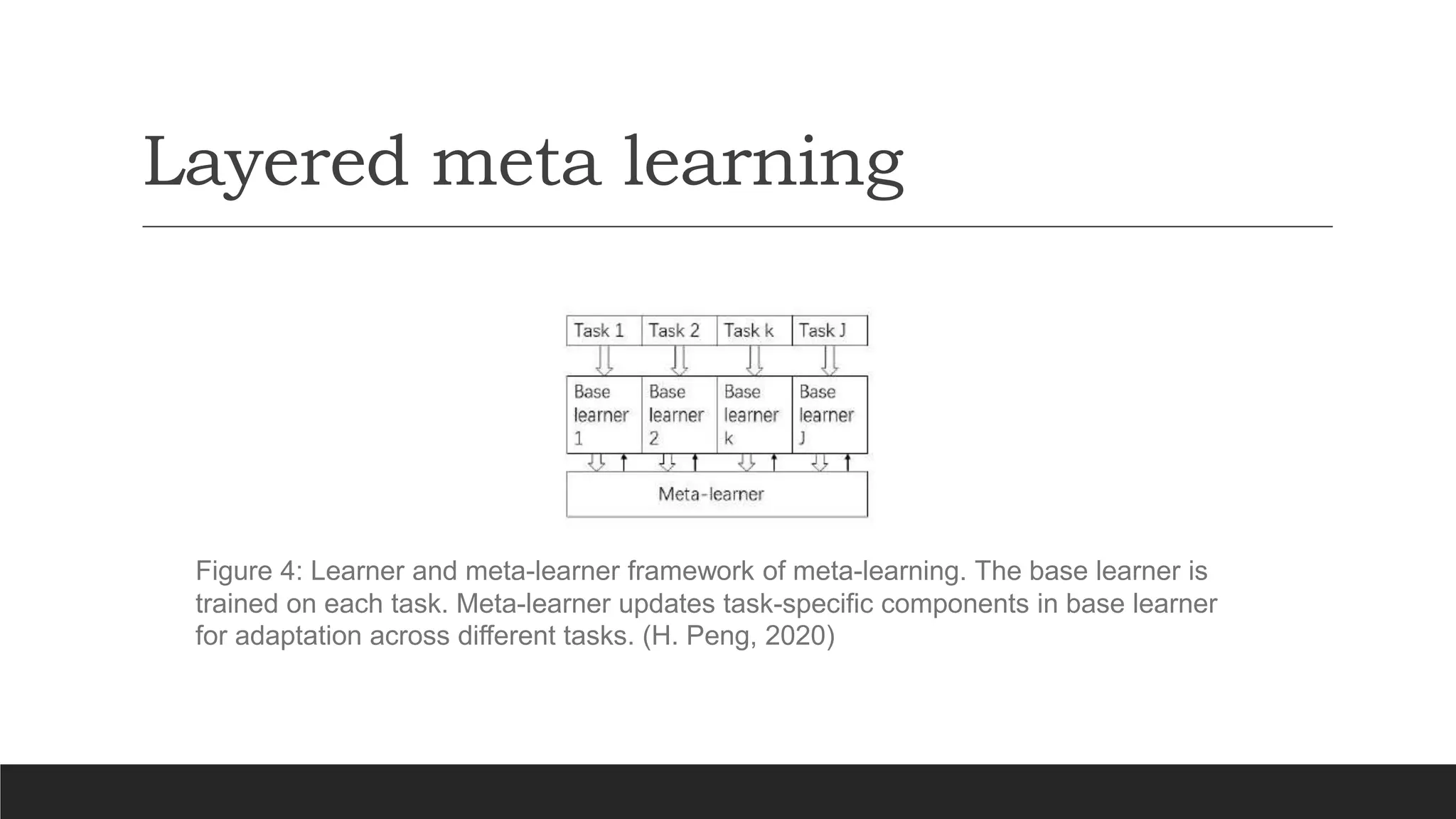
The document discusses a presentation on meta-learning based on a paper by Huimin Peng, detailing its definition and methodologies including black box, metric-based, layered, and Bayesian meta-learning. It highlights applications of meta-learning in areas such as robotics, automated trading, and drug discovery, while providing an overview of its framework and critique. The paper calls for improvements in understanding architectures and comparing benchmarks in various domains.

![References
This presentation is based on the paper “A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW AND SURVEY OF RECENT
ADVANCES IN META-LEARNING”, authored by Huimin Peng.
[1] H. Peng. A comprehensive overview and survey of recent advances in meta-learning (2020).
arXiv:2004.11149 [cs.LG].
[2] T. Hospedales, A. Antoniou, P. Micaelli, A. Storkey. Meta-Learning in Neural Networks: A Survey
(2020). arXiv:2004.05439 [cs.LG].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtolearnwithmetalearning-201102191538/75/Learning-to-learn-with-meta-learning-2-2048.jpg)