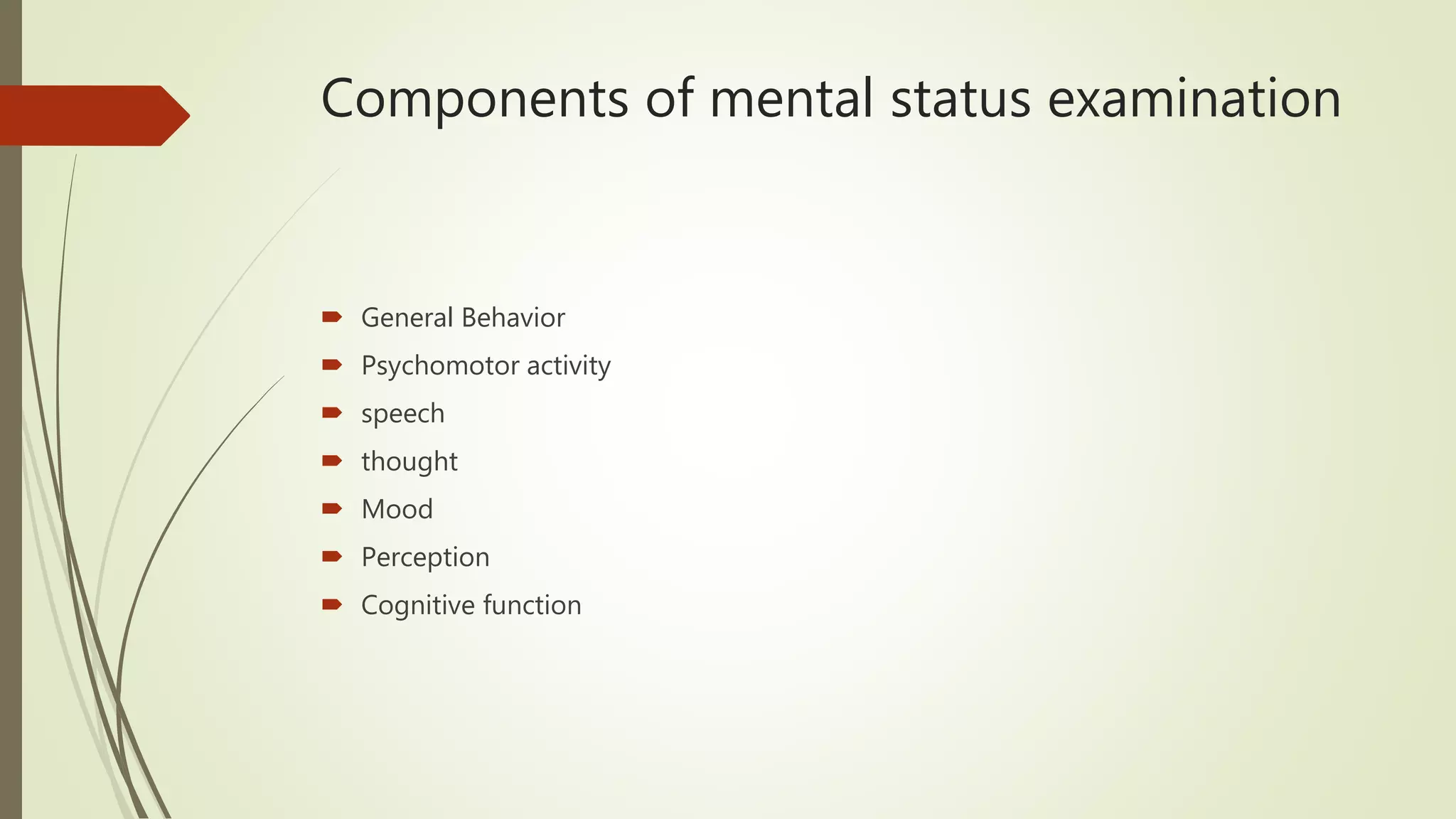
The document discusses the components and process of conducting a mental status examination. It describes the mental status examination as an assessment of a patient's cognitive abilities, appearance, mood, and speech patterns. The summary includes identifying data, appearance, behavior, mood, thought content, cognition, insight, and conclusion. The examination is used to obtain a comprehensive understanding of a patient's current mental state in order to make diagnoses and develop treatment plans.