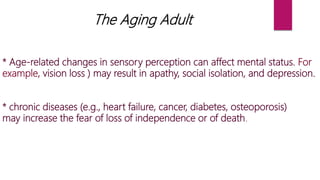
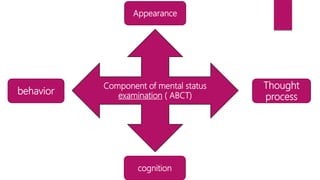
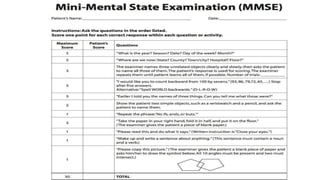
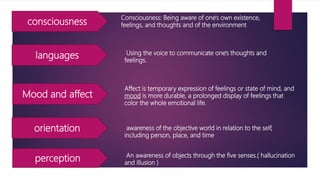
The document discusses mental status assessment. It defines mental status as a person's emotional and cognitive functioning, which allows them to function socially and occupationally. A traumatic life event can tip the balance of mental status and cause transient dysfunction. Assessing mental status during traumatic events can identify strengths and help individuals mobilize coping skills. Optimal functioning aims for life satisfaction in relationships, work, and within oneself. The document also discusses factors that can affect the interpretation of mental status examinations, such as medical conditions or medications. It provides details on components assessed in a mental status exam including appearance, behavior, mood, affect, orientation, and cognitive functions.









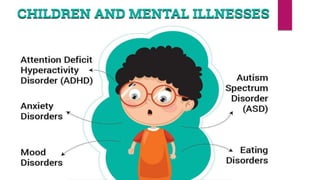
![. Adolescents ages childhood
mental disorder is one that is
diagnosed and begins in
childhood (e.g., attention
deficit/hyperactivity disorder
[ADHD], behavioral or conduct
problems, anxiety, depression,
autism spectrum disorders)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mentalstatusassessment-presentation2-211114210913/85/Mental-status-assessment-presentation-12-320.jpg)