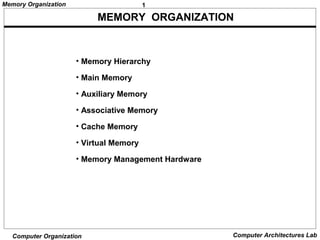
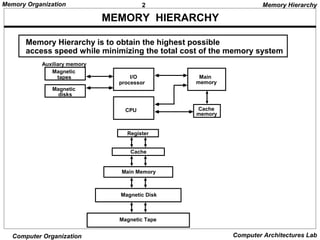
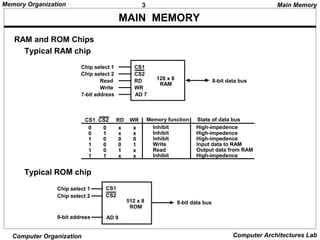
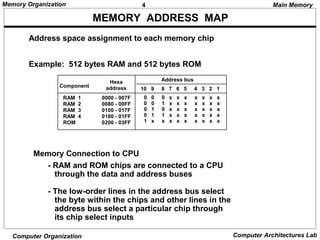
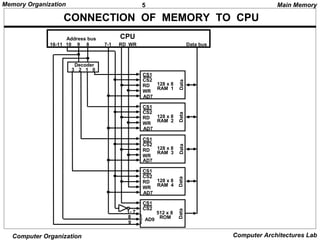
The document discusses different levels of computer memory hierarchy including main memory, cache memory, auxiliary memory, and virtual memory. Main memory uses RAM and ROM chips that are connected to the CPU through address and data buses. The address lines select the specific memory chip and byte location within that chip. Main memory is the highest level of memory that can be accessed directly by the CPU for storage of data and instructions currently in use.