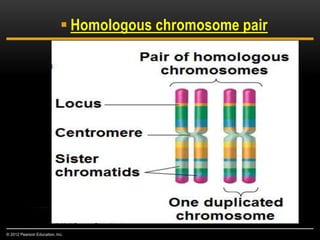
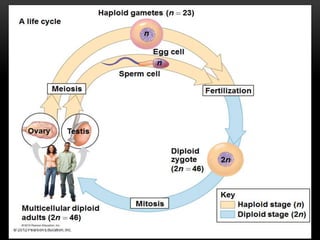
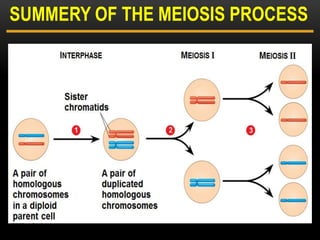
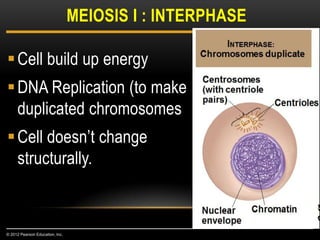
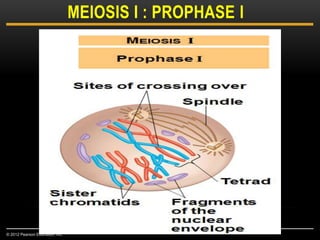
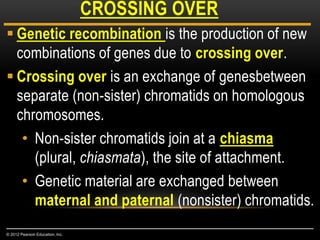
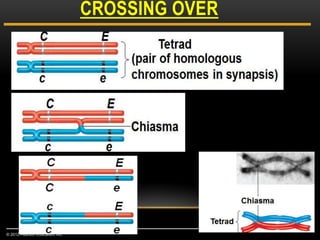
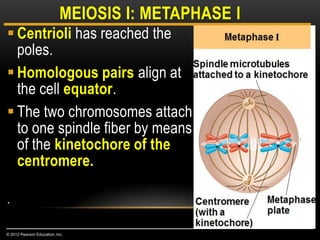
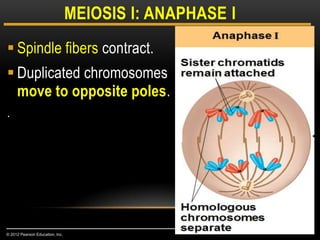
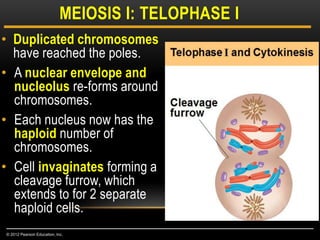
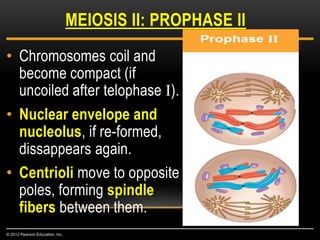
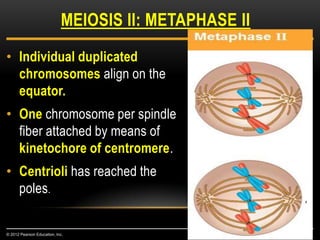
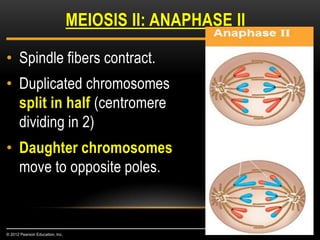
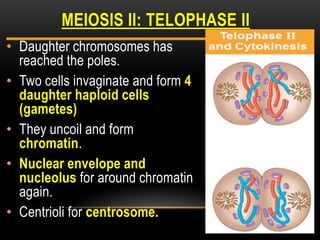
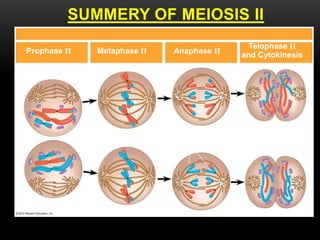
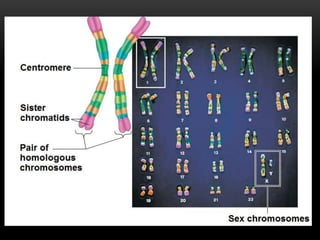
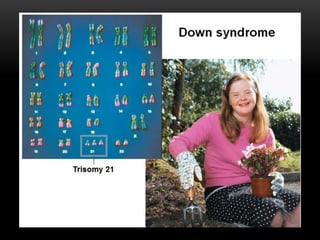
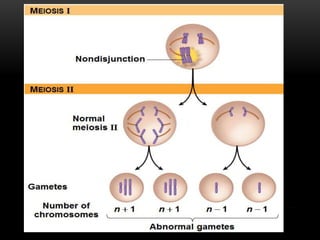
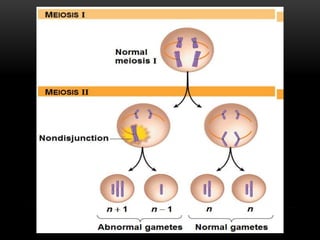
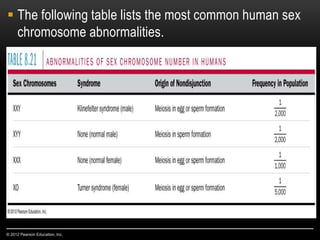
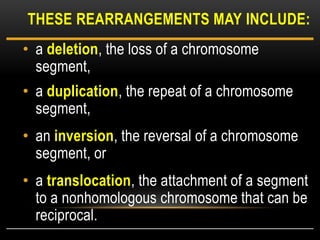
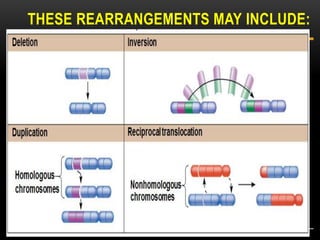
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces haploid gametes from diploid cells in two stages. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair and undergo crossing over, then separate. This reduces the chromosome number by half to produce haploid cells. Meiosis II then divides the contents of these haploid cells without further combining of homologs, resulting in four haploid gametes. Two gametes combine at fertilization to form a diploid zygote and complete the life cycle.