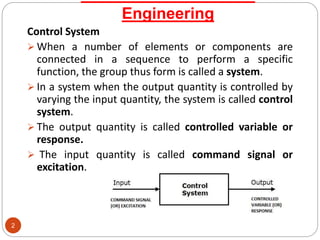
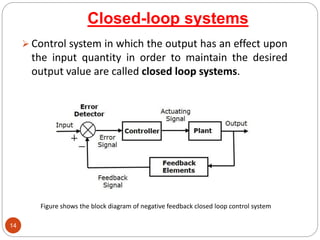
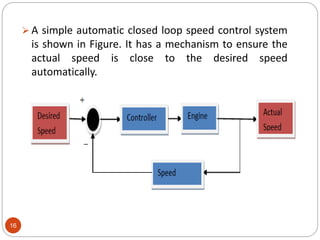
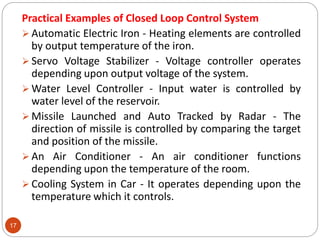
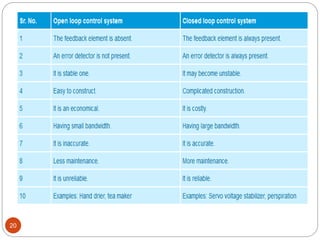
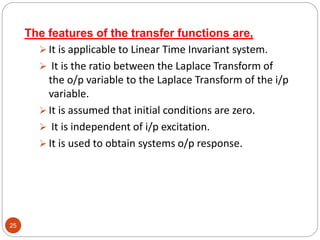
This document provides an overview of control systems engineering. It defines a control system as a group of connected elements that perform a specific function. A control system regulates the output of a system by adjusting the input. Control systems can be classified based on their analysis/design methods, signal types, system components, and purpose. Linear systems follow superposition principles while nonlinear systems do not. Time-invariant systems have parameters unaffected by time. Continuous and discrete systems have continuous or discrete signals. Single-input single-output and multiple-input multiple-output systems have one or multiple inputs/outputs. Feedback control systems have their output fed back to modify the input to monitor performance. Open-loop systems do not use feedback to control the output,