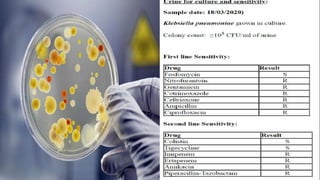
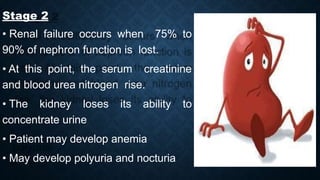
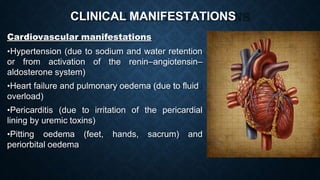
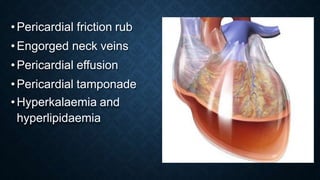
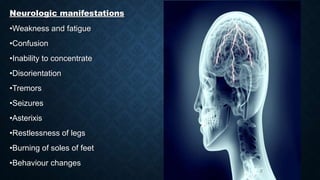
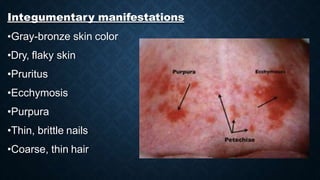
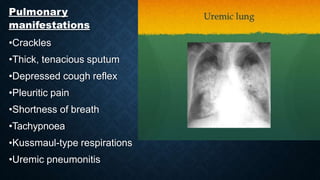
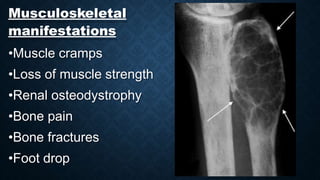
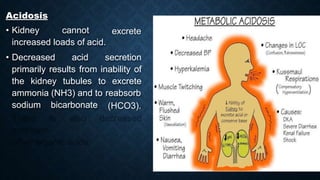
This document discusses end stage renal disease (ESRD), defined as a glomerular filtration rate below 15 mL/min. ESRD can result from chronic kidney diseases like diabetes or hypertension that damage the kidneys over time. As kidney function declines, waste products accumulate in the bloodstream, disrupting electrolyte and fluid balance. By stage 3/ESRD, the kidneys function at less than 10% capacity, requiring dialysis. Common complications include anemia, bone disease, heart problems, and fluid/electrolyte imbalances due to the kidneys' impaired ability to filter wastes and regulate balance.



![DEFINITION
Glomerular filtration rate [GFR] less than 60 mL/min and albumin greater than 30
mg per gram of creatinine along with abnormalities of kidney structure or function for
greater than three months signifies chronic kidney disease
End-stage renal disease is defined as a GFR of less than 15 mL/min.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrd-200430175414-230703035944-b35a4173/85/esrd-200430175414-pptx-5-320.jpg)