Gonadal hormone
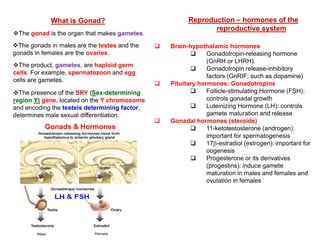
- 1. What is Gonad? The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes. The presence of the SRY (Sex-determining region Y) gene, located on the Y chromosome and encoding the testeis determining factor, determines male sexual differentiation. Reproduction – hormones of the reproductive system Brain-hypothalamic hormones Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH or LHRH). Gonadotropin release-inhibitory factors (GnRIF; such as dopamine) Pituitary hormones: Gonadotropins Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH): controls gonadal growth Luteinizing Hormone (LH): controls gamete maturation and release Gonadal hormones (steroids) 11-ketotestosterone (androgen): important for spermatogenesis 17-estradiol (estrogen): important for oogenesis Progesterone or its derivatives (progestins): induce gamete maturation in males and females and ovulation in females Gonads & Hormones
- 2. GonadalHormone in Male Gonadal Hormone in Female Ovulation and Corpus Luteum formation Luteinizing hormone (LH) In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. Hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland In females, an acute rise of LH ("LH surge") triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum It acts synergistically with FSH.
- 3. Structure of LH LH is a heterodimeric glycoprotein. Each monomeric unit is a glycoprotein molecule One alpha and one beta subunit make the full, functional protein. The alpha subunits of LH contain 92 amino acids in human but 96 amino acids in almost all other vertebrate species. The carbohydrate moiety is linked to the asparagine at positions 52 and 78. LH beta subunit have 120 amino acids (LHβ) that confers its specific biologic action and is responsible for the specificity of the interaction with the LH receptor. The biologic half-life of LH is 20 minutes, shorter than that of FSH (3–4 hours) and hCG (24 hours). Genes The gene for the alpha subunit is located on chromosome 6q12.21. The LH beta subunit gene is localized in the LHB/CGB gene cluster on chromosome 19q13.32. In contrast to the alpha gene activity, beta LH subunit gene activity is restricted to the pituitary gonadotropic cells. It is regulated by the gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus. Activity In both males and females, LH is essential for reproduction. In the male, LH acts upon the Leydig cells of the testis and is responsible for the production of testosterone, an androgen that exerts both endocrine activity and intratesticular activity on spermatogenesis.
- 4. LH is necessary to maintain luteal function for the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle. If pregnancy occurs, LH levels will decrease, and luteal function will instead be maintained by the action of hCG (a hormone very similar to LH but secreted from the new placenta). In females, LH supports theca cells in the ovary that provide androgens and hormonal precursors for estradiol production. At the time of menstruation, FSH initiates follicular growth, specifically affecting granulosa cells. With the rise in estrogens, LH receptors are also expressed on the maturing follicle, which causes it to produce more estradiol. When the follicle has fully matured, a spike in estrogen production by the follicle stimulates a positive feedback loop in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of LH from the anterior pituitary. This increase in LH production only lasts for 24 to 48 hours. This "LH surge" triggers ovulation, thereby not only releasing the egg from the follicle, but also initiating the conversion of the residual follicle into a corpus luteum that, in turn, produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for a possible implantation. Secretion pattern of LH
- 5. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) act synergistically in reproduction. Specifically, an increase in FSH secretion by the anterior pituitary causes ovulation. It is synthesized and secreted by gonadotrophs of the anterior pituitary gland. FSH regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH is a glycoprotein. Each monomeric unit is a protein molecule with a sugar attached to it; two of these make the full, functional protein. Its structure is similar to those of LH, TSH, and hCG. The protein dimer contains 2 polypeptide units, labeled alpha and beta subunits. The alpha subunits of LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG are identical, and contain 92 amino acids. The beta subunits vary. FSH has a beta subunit of 111amino acids (FSH β), which confers its specific biologic action and is responsible for interaction with the FSH- receptor. The half-life of FSH is 3–4 hours. Structure Activity FSH regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the human body. FSH enhances the production of androgen-binding protein by the Sertoli cells of the testes by binding to FSH receptors on their basolateral membranes, and is critical for the initiation of spermatogenesis. Effects in males FSH stimulates primary spermatocytes to undergo the first division of meiosis, to form secondary spermatocytes.
- 6. Effects in females FSH stimulates the growth and recruitment of immature ovarian follicles in the ovary. In early (small) antral follicles, FSH is the major survival factor that rescues the small antral follicles (2–5 mm in diameter for humans) from apoptosis (programmed death of the somatic cells of the follicle and oocyte). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), Also known as Luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) and luliberin, is a trophic peptide hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is synthesized and released from neurons within the hypothalamus. GnRH is considered a neurohormone, a hormone produced in a specific neural cell and released at its neural terminal. At the pituitary, GnRH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins, follicle- stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). Low-frequency GnRH pulses lead to FSH release, whereas high-frequency GnRH pulses stimulate LH release.
- 8. Testosterone Testosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testicles of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands. It is the principal male sex hormone and an anabolic steroid. In men, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as the testis and prostate as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle, bone mass, and the growth of body hair. Testosterone Biosynthesis of testosterone The largest amounts of testosterone (>95%) are produced by the testes in men. It is also synthesized in far smaller quantities in women by the thecal cells of the ovaries, and by the placenta, The zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex and skin in both sexes also produces in small quantities. In the testes, testosterone is produced by the Leydig cells. The male generative glands also contain Sertoli cells which require testosterone for spermatogenesis.
- 9. Testosterone is primarily synthesized in Leydig cells. The number of Leydig cells in turn is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). The amount of testosterone produced by existing Leydig cells is under the control of LH which regulates the expression of 17-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD). When testosterone levels are low, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released by the hypothalamus which in turn stimulates the pituitary gland to release FSH and LH. These later two hormones stimulate the testis to synthesize testosterone. Finally increasing levels of testosterone through a negative feedback loop act on the hypothalamus and pituitary to inhibit the release of GnRH and FSH/LH respectively. Regulation of Testosterone Biosynthesis Biosynthesis of Estrogen: Estrogens, in females, are produced primarily by the ovaries, and during pregnancy, the placenta. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the ovarian production of estrogens by the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles and corpora lutea. Some estrogens are also produced in smaller amounts by other tissues such as the liver, adrenal glands, and the breasts. In females, synthesis of estrogens starts in theca interna cells in the ovary, by the synthesis of androstenedione from cholesterol.
- 10. Estrogen Estriol Estradiol Estrone They are the primary female sex hormones. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors which in turn modulate the expression of many genes. Additionally, estrogens have been shown to activate a G protein-coupled receptor, GPR30. Estradiol is the predominant estrogen during reproductive years During menopause, estrone is the predominant circulating estrogen during pregnancy estriol is the predominant circulating estrogen Function of Estrogen Promote formation of female secondary sex characteristics Accelerate metabolism Increase fat stores Stimulate endometrial growth Increase uterine growth Increase vaginal lubrication Thicken the vaginal wall Maintenance of vessel and skin Reduce bone resorption, increase bone formation Reduce muscle mass
- 11. Progesterone Progesterone also known as P4 (pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione) is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species. Progesterone belongs to a class of hormones called progestogens, and is the major naturally occurring human progestogen. Progesterone is produced in the ovaries (by the corpus luteum), the adrenal glands and, during pregnancy, in the placenta. Progesterone is also stored in adipose (fat) tissue. Progesterone Level of Progesterone In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, rise after ovulation, and are elevated during the luteal phase, as shown in diagram below. Progesterone levels tend to be < 2 ng/ml prior to ovulation, and > 5 ng/ml after ovulation. If pregnancy occurs, human chorionic gonadotropin is released maintaining the corpus leuteum allowing it to maintain levels of progesterone.
- 12. HYPOTHALAMUS RELEASES GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH). This stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH. FSH STIMULATES MATURATION OF PRIMARY OOCYTE IN AN IMMATURE FOLLICLE. FOLLICLE PRODUCES ESTROGEN. Estrogen: (A) builds the uterine wall (the endometrium); (B) inhibits secretion of FSH. HIGH LEVELS OF ESTROGEN FURTHER STIMULATE SECRETION OF LH BY ANTERIOR PITUITARY. This plus FSH also causes ovulation of the secondary oocyte – leaving follicle without egg (the corpus luteum). CORPUS LUTEUM SECRETES ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE. This maintains the endometrium for 15-16 days and inhibits LH. (If oocyte is not fertilized and implanted in the uterine wall) CORPUS DEGENERATES (TO CORPUS ALBICANS) AND STOPS PRODUCING ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE. WITHOUT ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE, ENDOMETRIUM BREAKS DOWN – MENSTRUATION OCCURS. Menstruation is the sloughing off of the enlarged endometrial wall along with blood and mucous. DECREASE IN PROGESTERONE AND LH. Low LH causes secretion of FSH by pituitary again. The cycle repeats. HORMONAL REGULATION IN NONPREGNANT FEMALE (UTERINE CYCLE)
