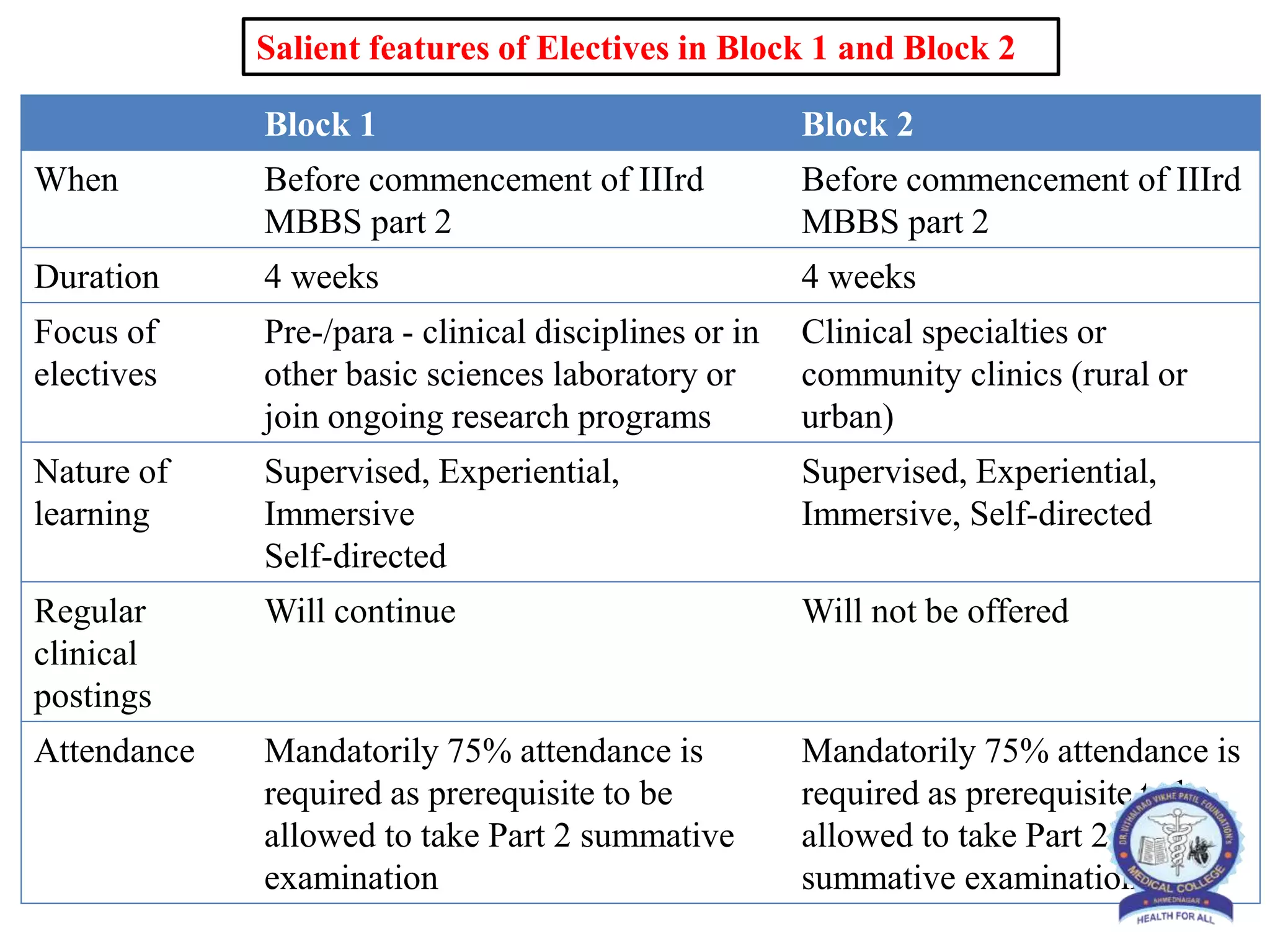
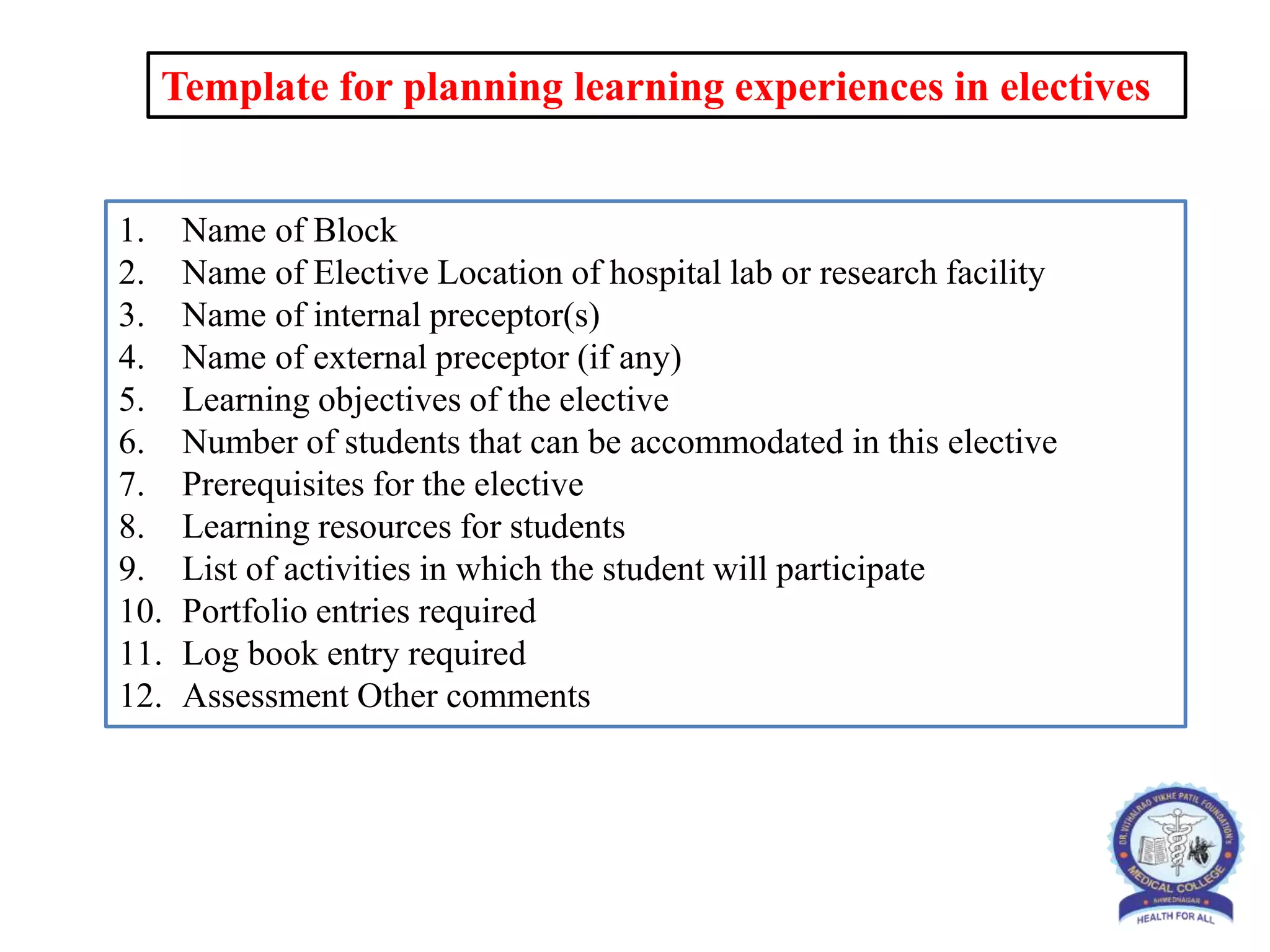
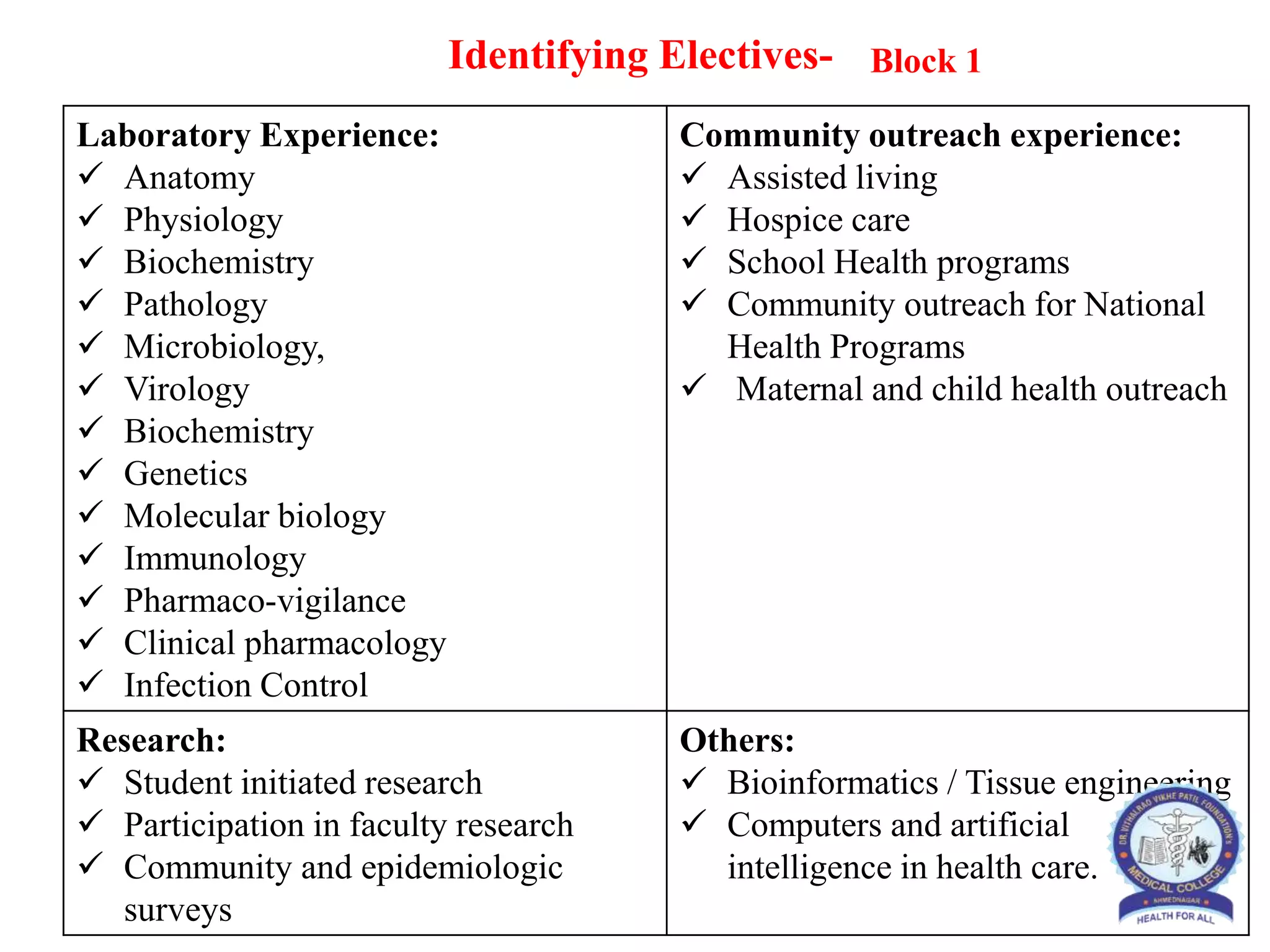
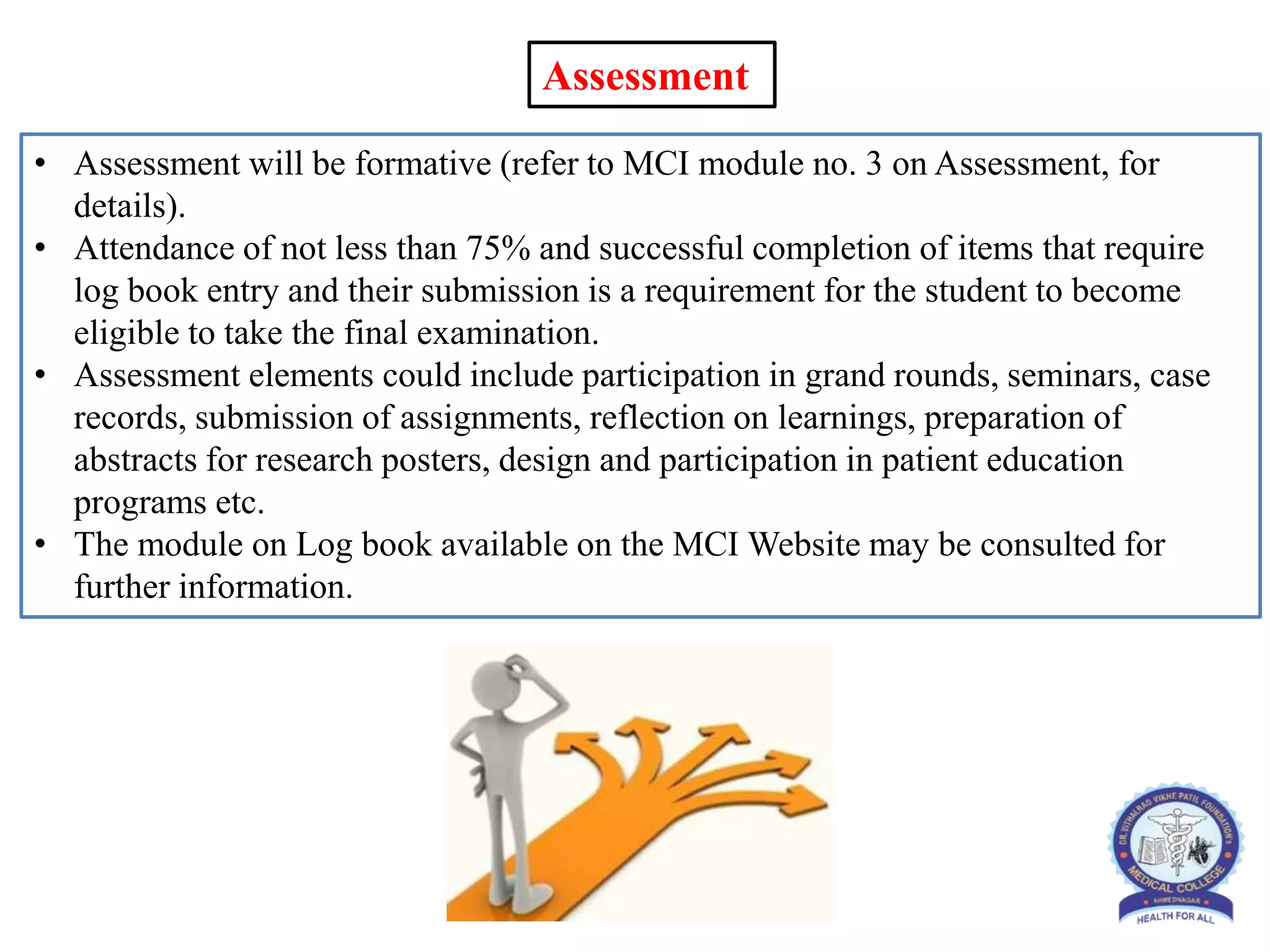
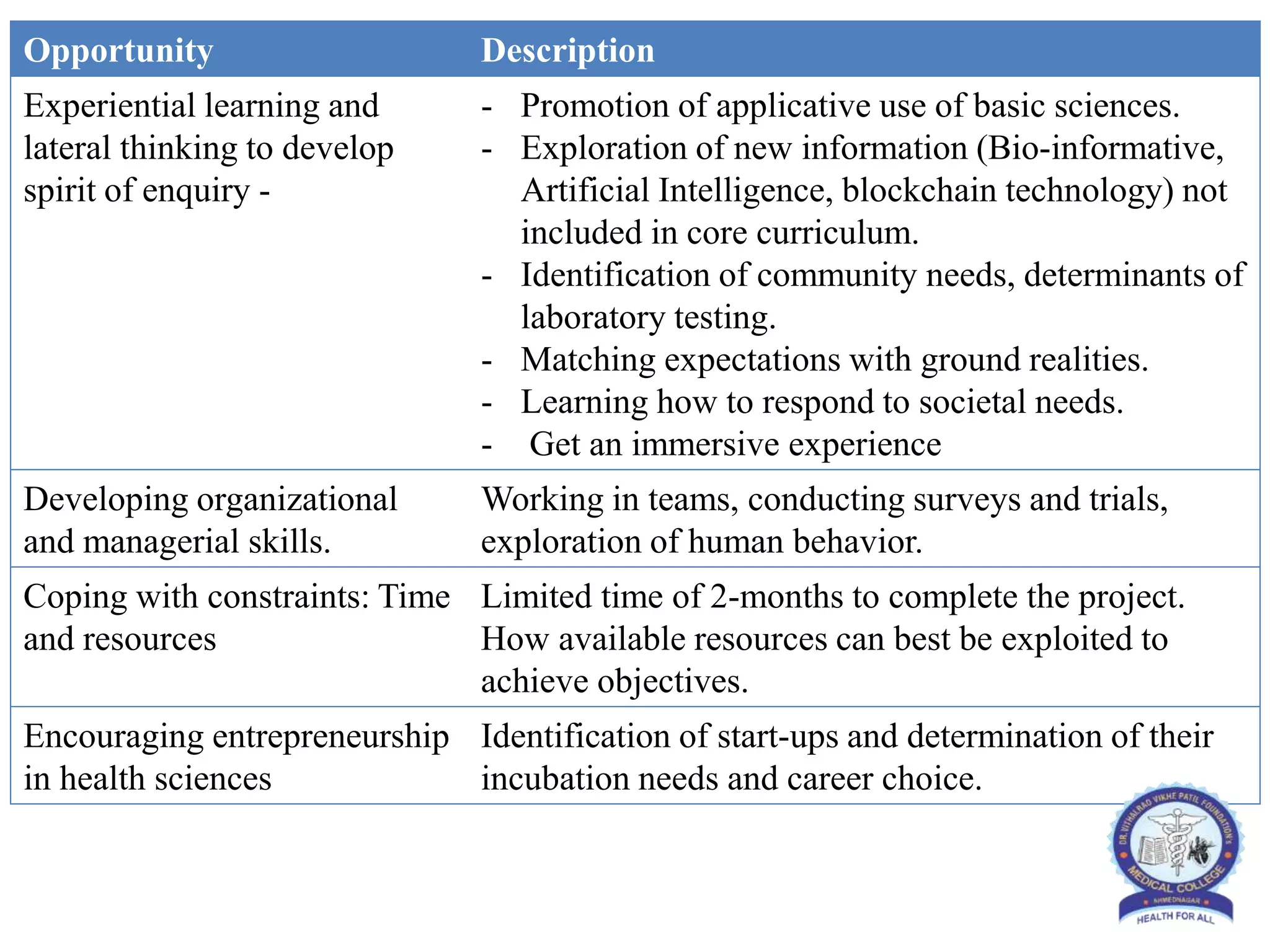
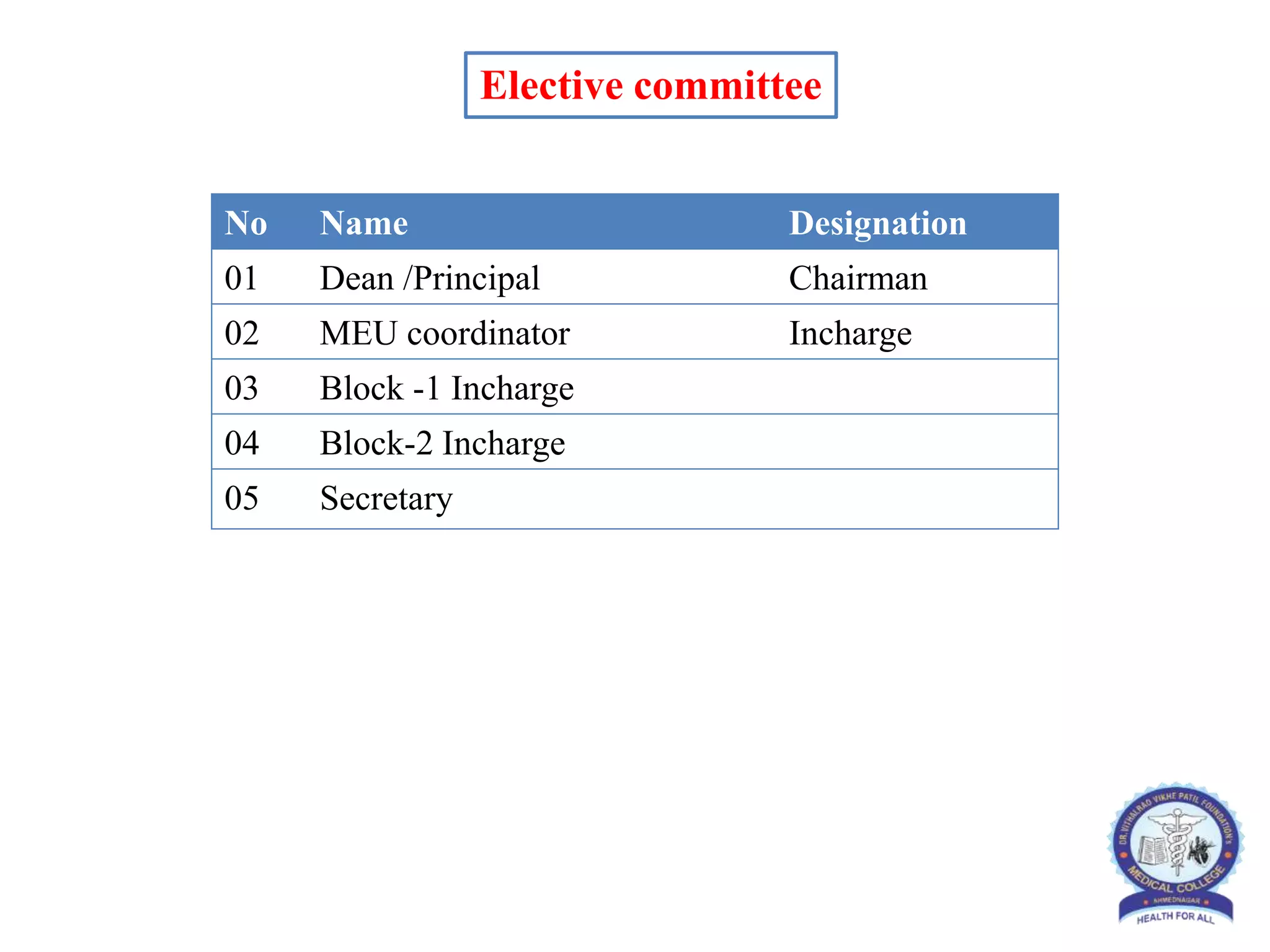
This document provides information and guidelines regarding medical electives for undergraduate medical students in India. It defines electives as optional learning experiences that allow students to explore areas of interest. The document outlines the objectives and structure of elective blocks, including topics that can be covered, requirements for attendance, supervision, and assessment. It provides templates for planning elective learning experiences and identifying potential electives in different areas like laboratories, research, clinical specialties, and community settings. The goal is to provide immersive, experiential learning opportunities to help students discover career paths and develop skills beyond their curriculum.